An SD card that keeps disconnecting can be tricky to diagnose. It could be something banal, like outdated drivers, or a damaged card reader. On the other hand, this can also indicate serious issues like SD card failure, worn-out contacts, and physical damage.
You likely have several questions. Why does my SD card keep disappearing? Is it possible to fix the SD card? If yes, how? How do I recover my data from the SD card? The sections below answer all of these in detail—several users successfully resolved the issue using the recommended methods, and we’ve tested each one to confirm it works.
Why Does My SD Card Keep Ejecting Itself?
Believe it or not, randomly disconnecting and reconnecting SD cards are a common issue faced by users across different platforms. However, you’re more likely to run into the issue on Windows computers, and recently, Steam Decks as well.
Here are some potential reasons why your SD card keeps ejecting:
- 📛 Faulty SD Card Reader: Maybe you skimped on the SD card reader. After all, it’s the SD card that’s important, right? Well, yes. But lower-quality SD card readers can malfunction at any time, impeding the connection between your SD card and the computer. This issue impacts in-built SD card readers as well.
- 💥 Damaged Contacts and Ports: Your SD card has copper contacts that help it communicate with the host device—it could be an internal SD card slot or a card reader. These contacts are prone to oxidation, wear and tear, and other types of physical damage. If it’s bad enough, your SD card may frequently disconnect, or not show up at all. USB ports, too, are susceptible to physical damage over time—which prevents them from reading an SD card via a card reader.
- ⚙️ Outdated, or Faulty Software Drivers: Your SD card and the card reader communicate with your PC’s operating system using drivers. Windows typically updates these drivers automatically, but there can be exceptions. Outdated drivers that are incompatible with newer software (like a new version of Windows) on your PC can cause problems like the SD card disconnecting frequently Sometimes, your OS may install a faulty (albeit new) version of a driver that causes the same issue.
- 🧰 Faulty Windows Updates: If you recently updated Windows, and then ran into the SD card disconnecting issue—the fault could be with the update itself. Uninstalling the latest updates and reconnecting the SD card is the only way to confirm this.
- 🔋 Power Plan Settings: Depending on the power plan Windows is using, it may suspend specific inactive USB ports to conserve battery life/draw less power—thanks to the USB Selective Suspend feature. If your SD card is connected to your PC using one of these USB ports, it will keep disconnecting when not in use.
- 🕹️ SD Card Controller Issues: Controllers are chips responsible for managing data transfers between your SD card’s NAND flash memory, and your computer or any other host device. A damaged controller prevents your SD card from communicating properly with your computer, resulting in frequent disconnects, and other problems. If your SD card disconnects when copying files, this is likely the issue.
- 🔖 Counterfeit SD Cards: Fake SD cards are a dime a dozen. And if you have one, it’s likely to fail early because it’s made of low-quality materials. If you notice your SD card is relatively new, yet disconnects and reconnects on its own accord, it could be a sign that it’s failing.
The likelihood of fixing an SD card that keeps disconnecting depends on what’s causing the problem.
Generally, physical damage is difficult to fix, and shouldn’t be attempted unless you know what you’re doing. Cleaning an SD card’s contacts may help if dirty contacts are the reason for frequent disconnection. However, there’s little you (or anyone) can do about a broken SD card controller, or fried NAND flash chips. Damage that’s limited to software, or logical damage is usually easier to undo.
But before you actually repair the SD card, back up its data so you don’t lose your files when fixing it. I’ll take you through this process in the next section.
How to Back Up and Recover Data from Your SD Card
Data recovery is fairly straightforward in data loss scenarios like accidental deletion—just scan the SD card using a capable data recovery program. But that’s not possible when the SD card keeps disconnecting. Here, you first need to create a disk image—essentially a soft copy—of the SD card, and then scan the disk image using a data recovery program.
But why create a disk image in the first place? There are several reasons:
- Risk of corruption: If your SD card disconnects mid-copying, the copied file will often be corrupt. It may not affect the original file, but you’ll need to begin copying the file again. Couple that with large file sizes, and the whole process becomes more tedious than it should be.
- Preserving your data: A frequently disconnecting SD card can fail at any time. Once that happens, DIY data recovery methods won’t work, and even data recovery professionals can’t guarantee data recovery. Creating a disk image while the card is still working ensures that you don’t lose access to your files even if the SD card fails.
- Protection against unintended data loss: Some SD card repair methods—like running CHKDSK—can cause data loss as collateral damage. Creating a disk image keeps your data safe in such instances.
I’d suggest using Disk Drill to create a disk image. In addition to being extremely easy to use, it automatically resumes the disk creation process when your SD card reconnects after disconnecting. With frequent disconnections, this is the only sure-shot way of creating the disk image. You can then scan the disk image using Disk Drill itself. The program tops several lists of the best data recovery programs, so you can rest assured that you will get your data back.
Note: Disk Drill lets you recover up to 500 MB of data for free on Windows. Further recovery requires an upgrade to Disk Drill PRO, which is a one-time purchase.
Part 1: Creating a Disk Image Using Disk Drill
- Download and install Disk Drill.
- Connect your SD card to the computer.
- Open Disk Drill, and click on Byte-to-byte Backup, under Extra tools.
- Select your SD card from the list, and click on the Byte-to-Byte Backup button.
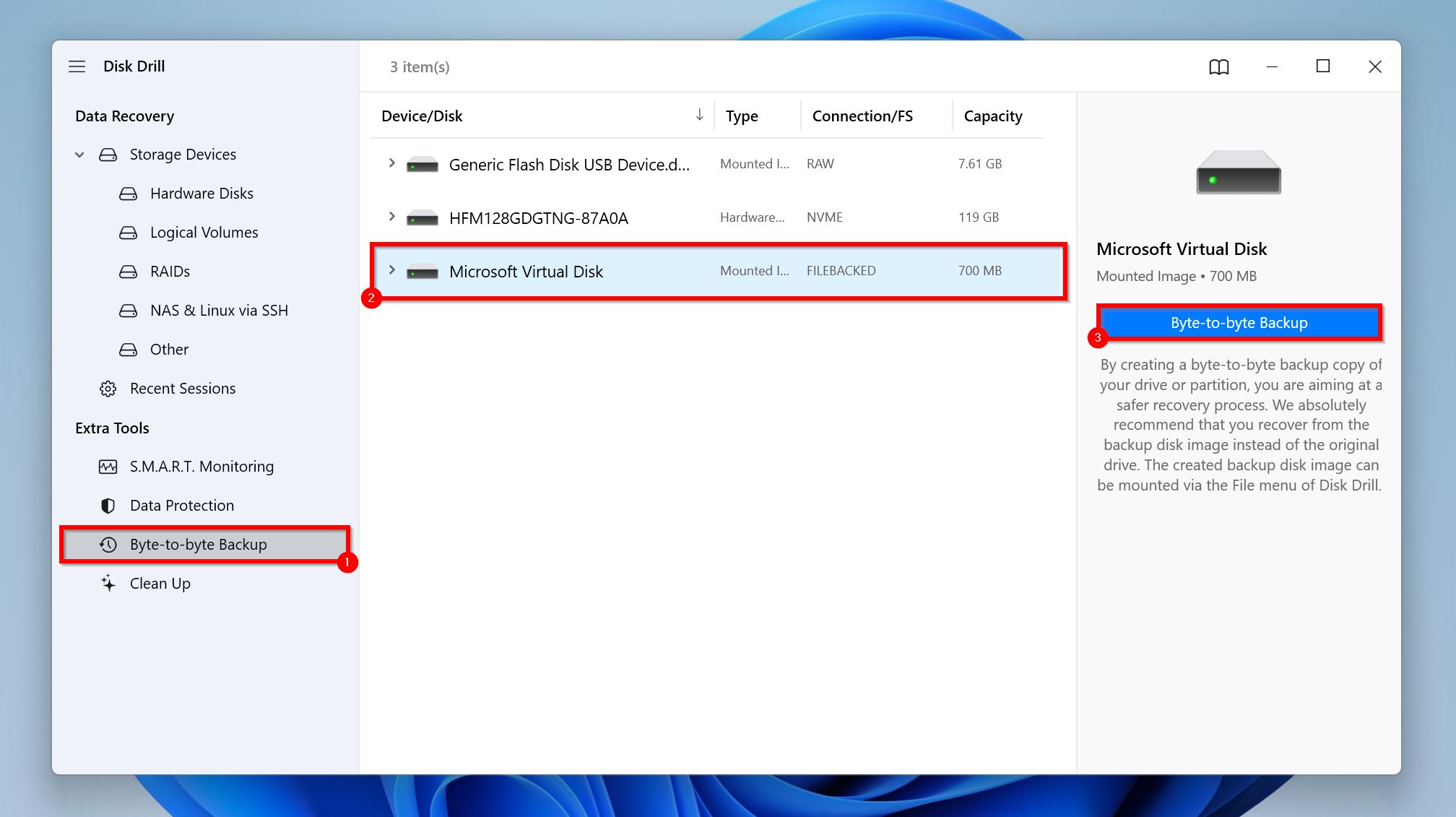
- Choose where you want to save the disk image and click OK. The destination should have enough free space (at least as much as the SD card’s entire storage capacity).
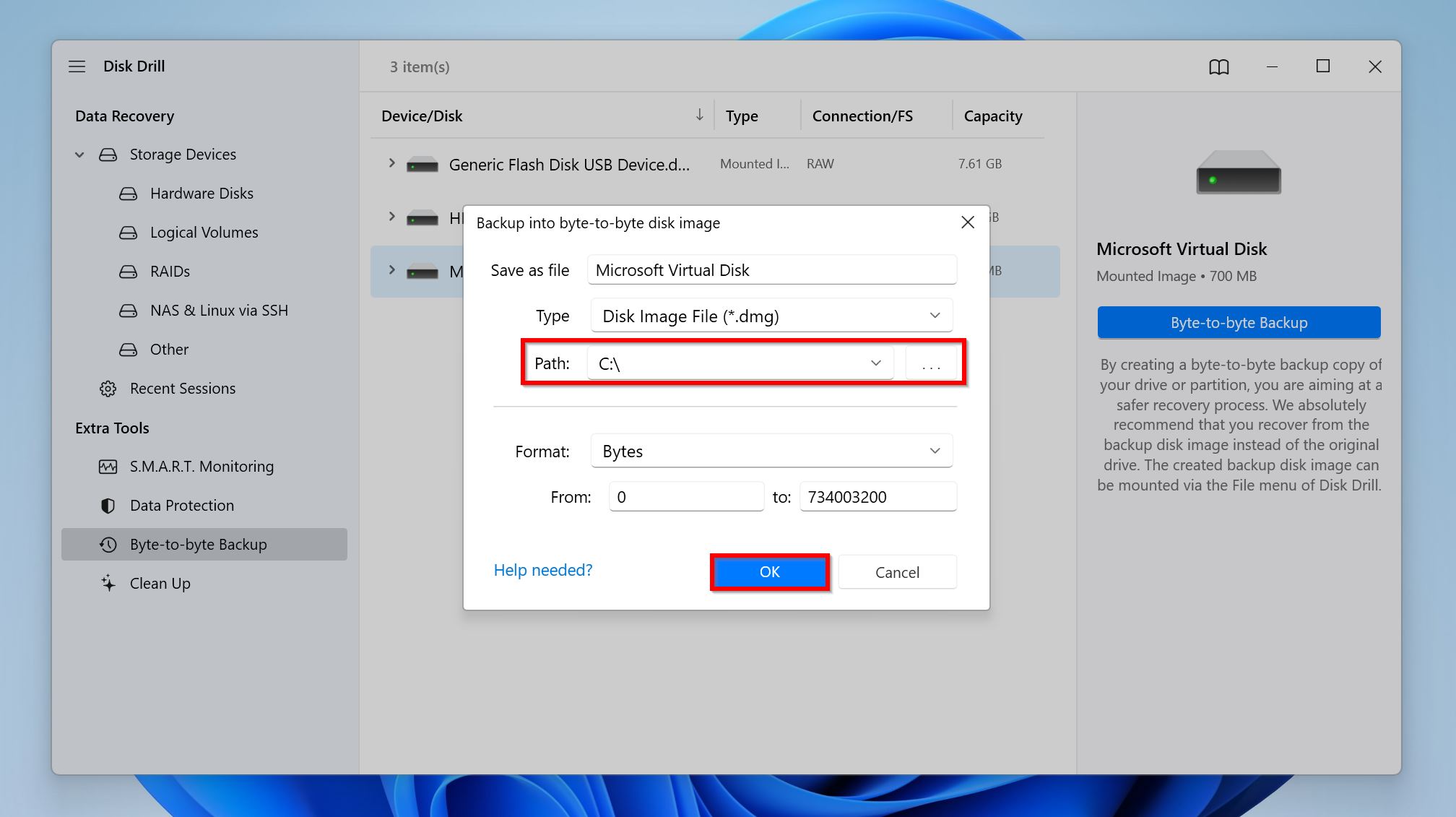
- Disk Drill will begin creating the disk image. If the SD card disconnects, simply reconnect it and Disk Drill will resume where it left off. This may take a while, so hang on!
Part 2: Scanning the Disk Image Using Disk Drill
Scanning the disk image instead of directly scanning the SD card offers two main advantages:
- The data recovery scan isn’t interrupted by the frequent disconnection of the SD card.
- Data recovery scans are stressful for the storage drive being scanned. Scanning the disk image prevents further damage to an already malfunctioning SD card. It lets you perform multiple scans without worrying that the SD card will stop working.
Here’s how to scan the SD card’s disk image using Disk Drill:
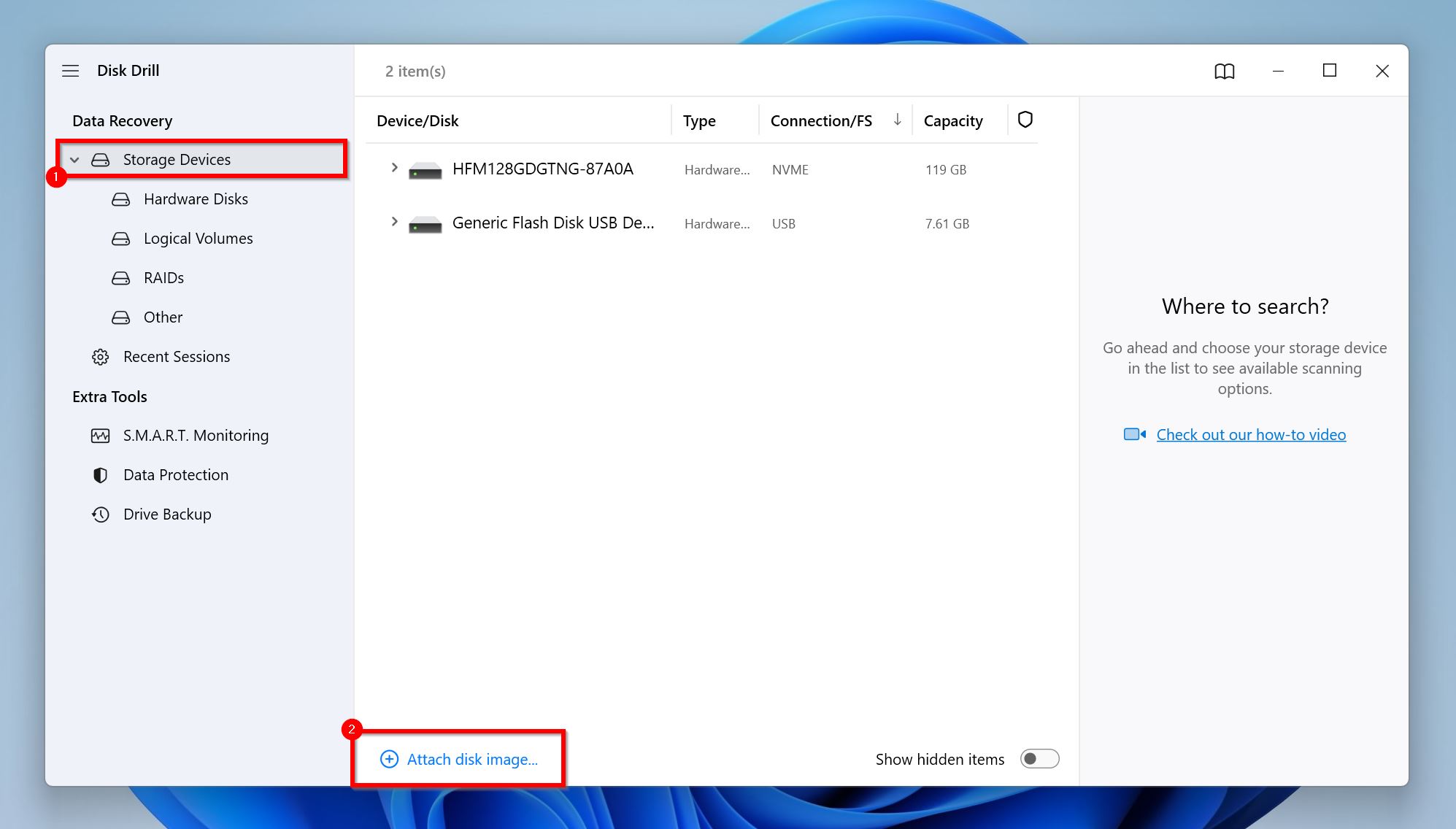
- Open Disk Drill, and click on the Storage Devices tab, under Data Recovery.
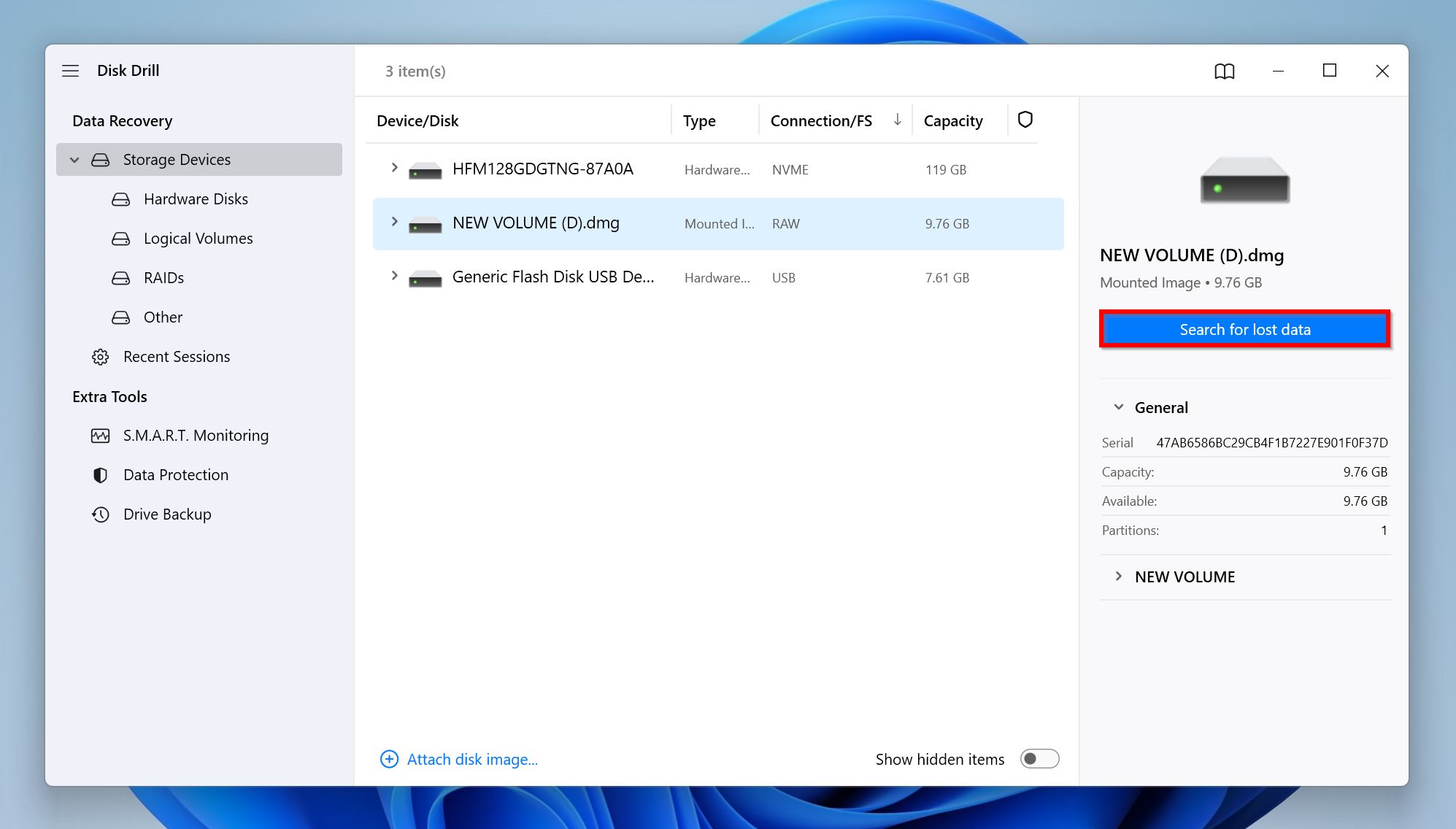
- Click on Add disk image at the bottom of the screen. Browse for the SD card’s disk image, and click Open. Disk Drill will mount the disk image, and it’ll show up in the storage devices list.
- Select the SD card’s disk image, and click Search for lost data.
- Click on Review found items once Disk Drill finishes scanning the drive. Wish to filter out the results? Simply click on the relevant file type tile instead (Pictures, Videos, Audio, Documents, Archives, and Other).
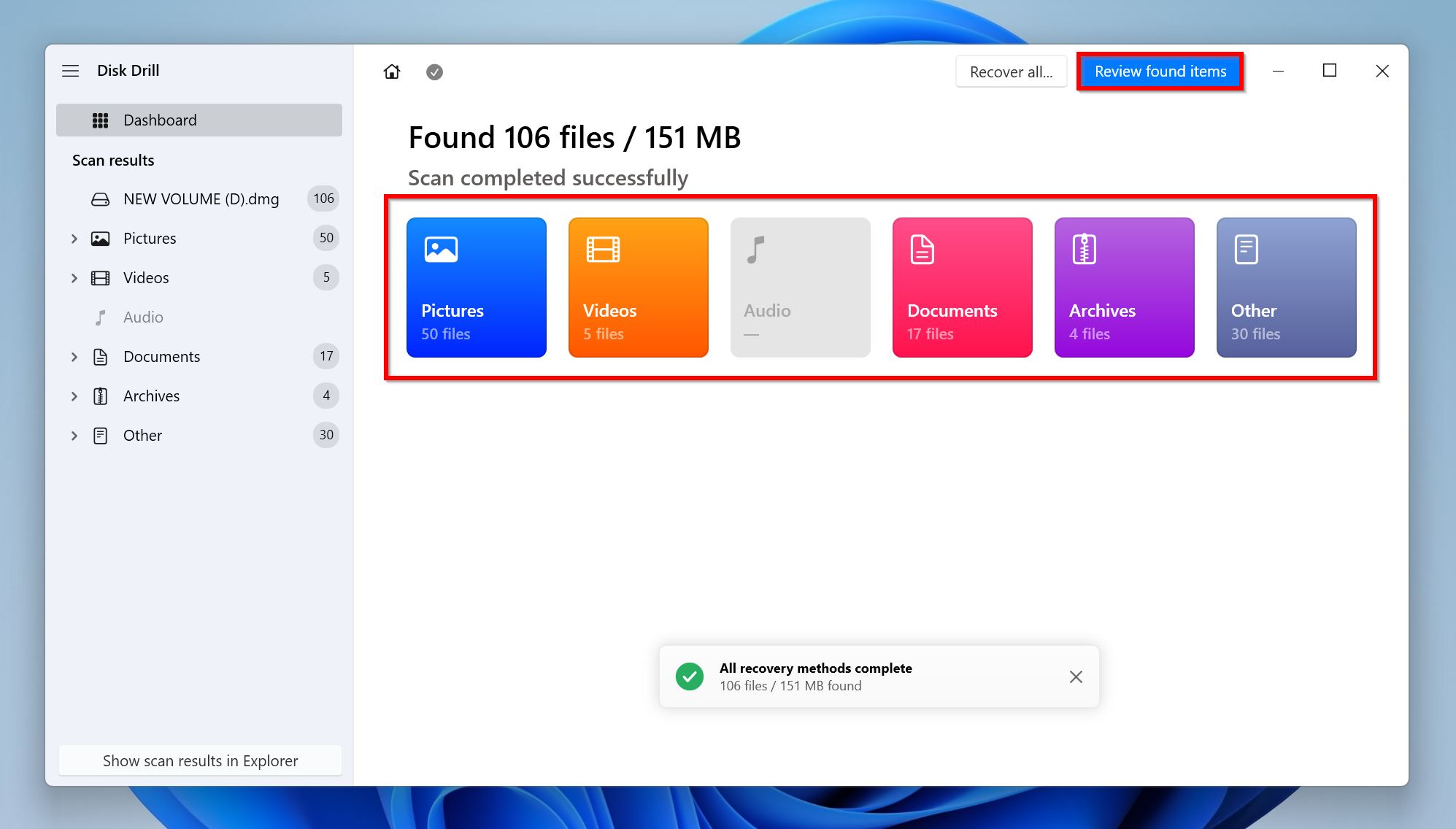
- Expand the Existing section to view currently stored files on the SD card. To view deleted files, expand the Deleted or lost, and Reconstructed sections instead.
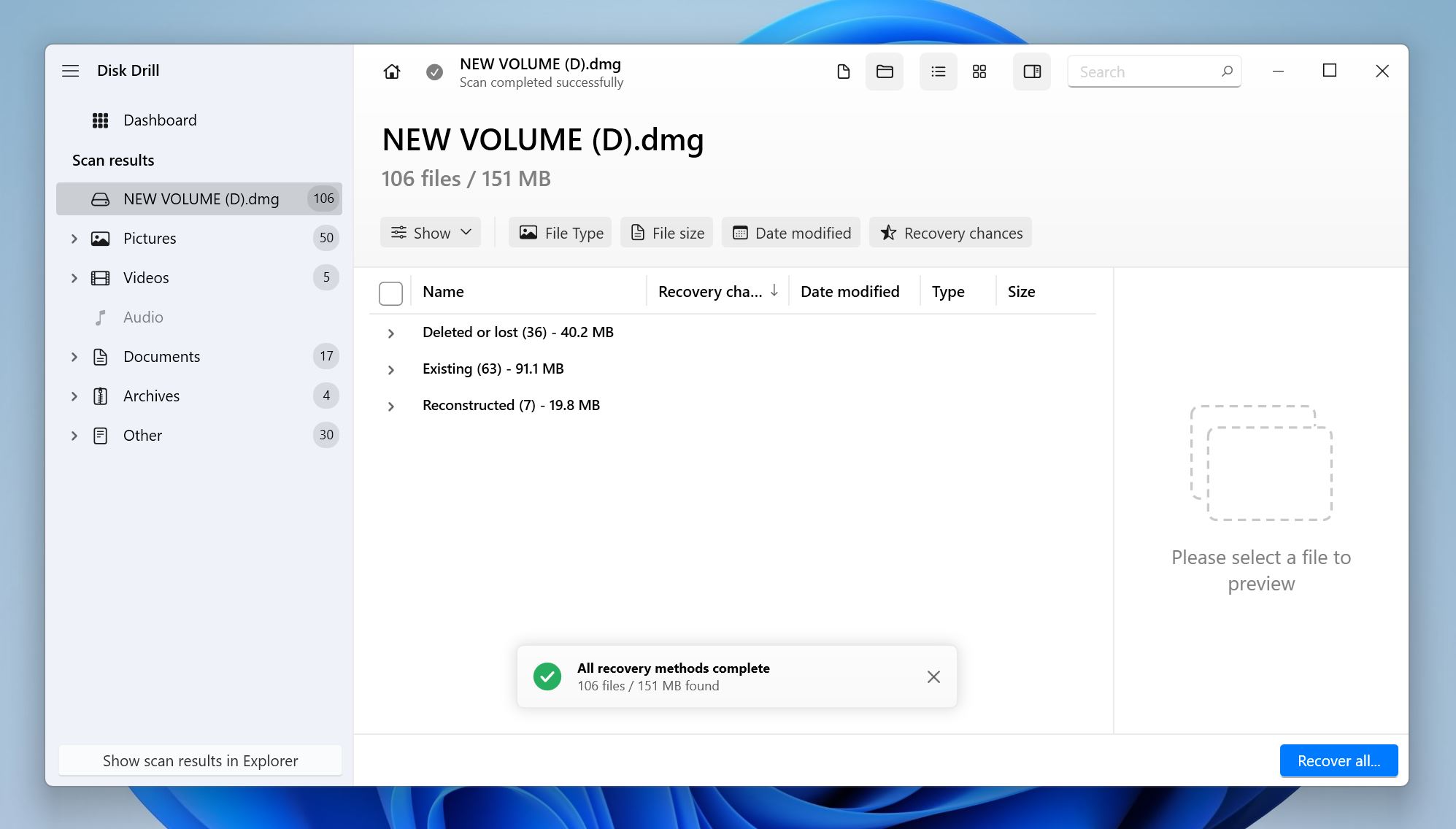
- Select the files you wish to recover. Disk Drill automatically displays a preview of the currently selected file, but you can manually preview any file by clicking the eye icon next to its filename. Once you’re done selecting, click on Recover.
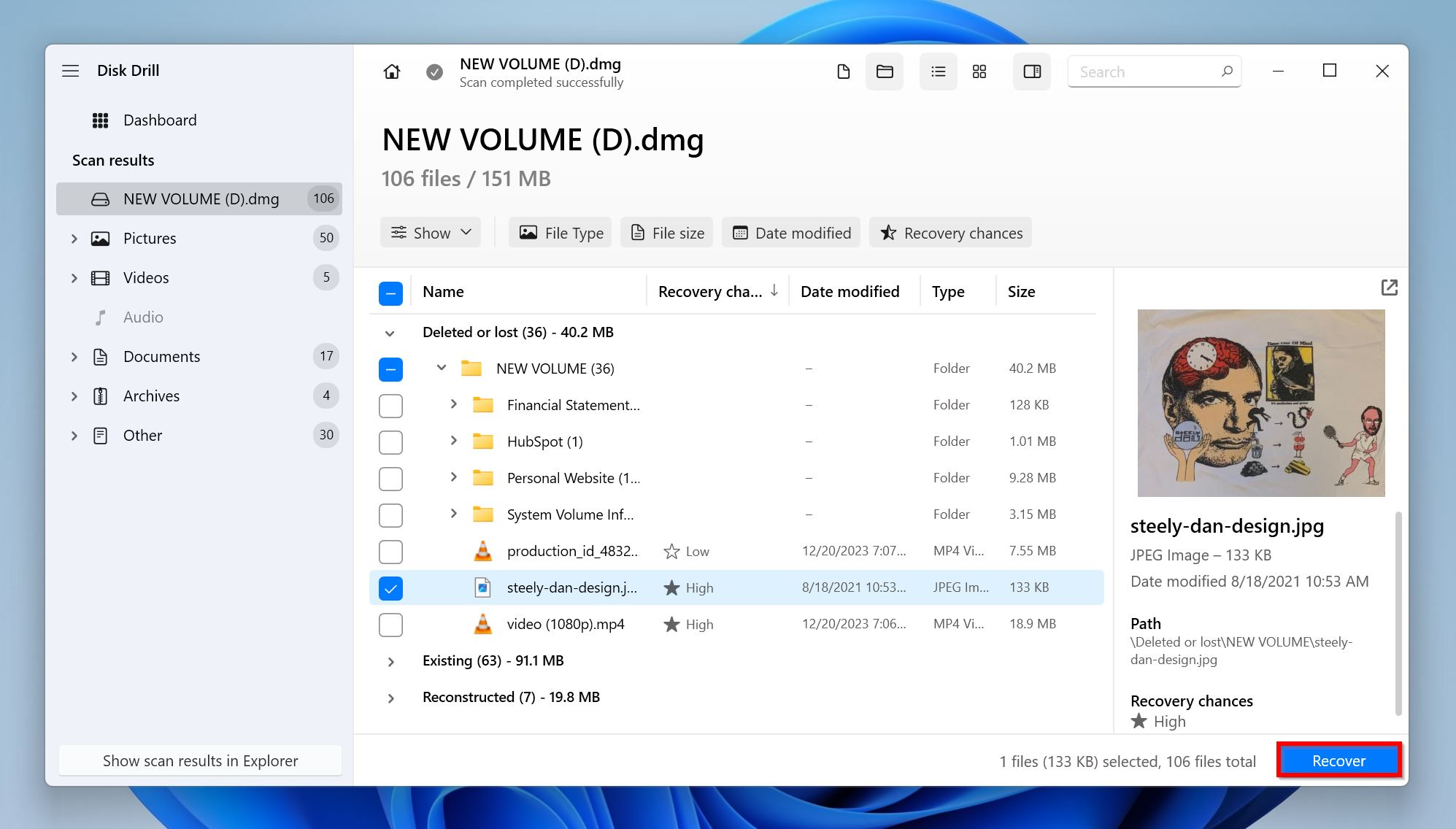
- Choose a recovery destination for the files, and click Next.
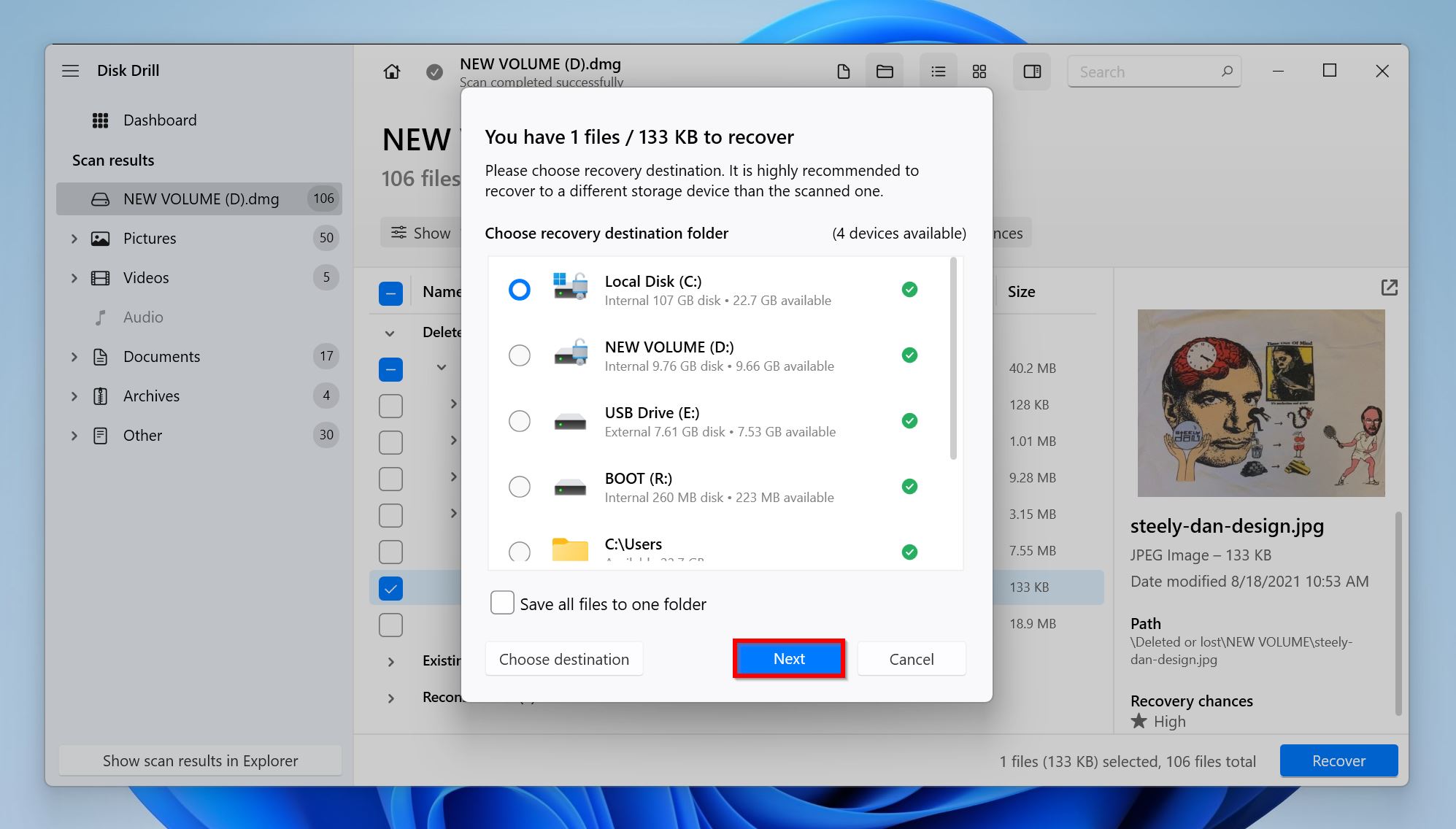
- Disk Drill will recover the selected files.
How to Fix an SD Card That Keeps Disconnecting
Before fixing an SD card that keeps ejecting, confirm that the problem actually lies with the SD card, and not the other components. Here’s how to confirm this:
- Use a different SD card reader and check if the problem remains.
- Remove your SD card and insert it into another PC using a different card reader. See if the issue persists, if it doesn’t, the problem likely lies with your PC, or its SD card slot/USB port.
- Try connecting the SD card to an in-built SD card slot on a laptop, or a camera. If it still behaves the same way, the SD card itself has an issue.
If the SD card keeps disconnecting, even after executing the steps above, proceed to fix the problem using the methods below.
Method 1: Update/Reinstall SD Card Drivers
Updating your SD card, and SD card reader drivers is the first fix you should attempt. Doing so can resolve a range of SD card related errors, including its frequent disconnection.
In case you updated the drivers recently, try reinstalling them to see if it fixes the issue.
Here’s how to update, or reinstall SD card drivers on Windows:
Update SD Card Drivers
- Type device manager in Windows Search (Windows Key + S). In the search results, click on the Device Manager app to open it.
- Expand the Disk Drives menu tree, right-click on the SD card, and choose Update driver.
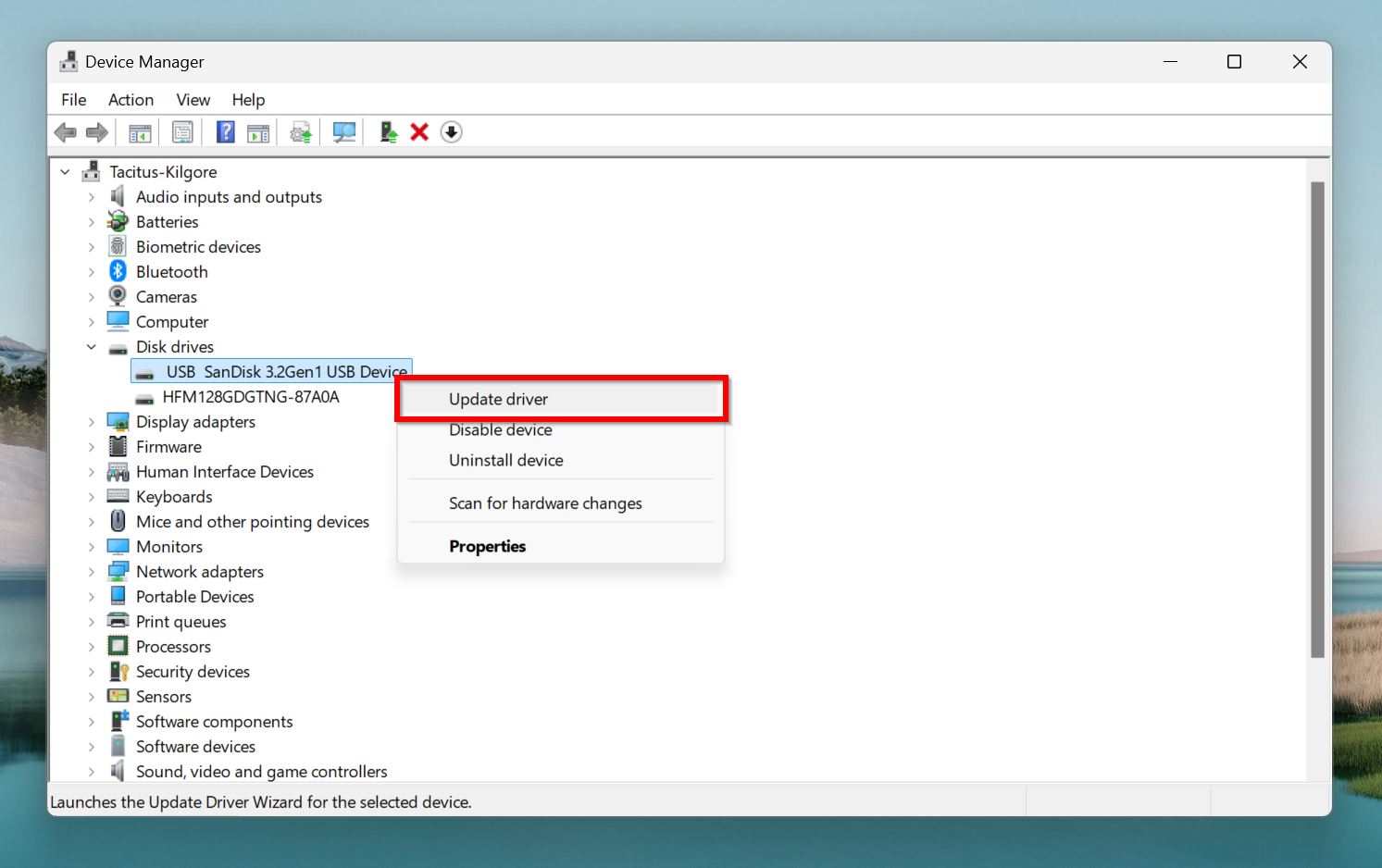
- Click on Search automatically for drivers. Windows will automatically find the latest drivers and install them.
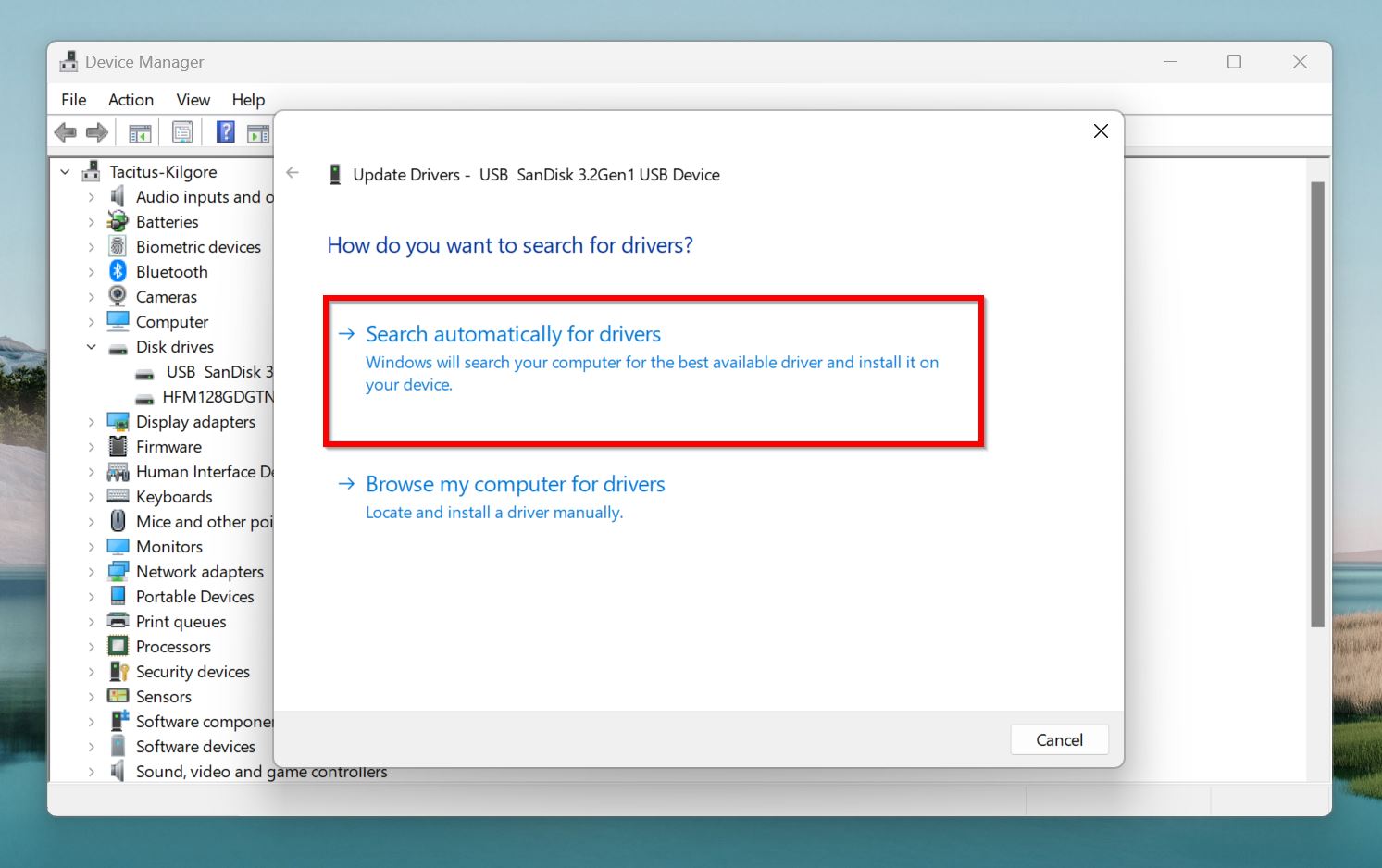
- Next, find the SD card reader in the devices list. It’ll be in the Disk Drives,Universal Serial Bus Controllers, or Memory Technology Drivers sections. Right-click on the SD card reader, and choose Update driver.
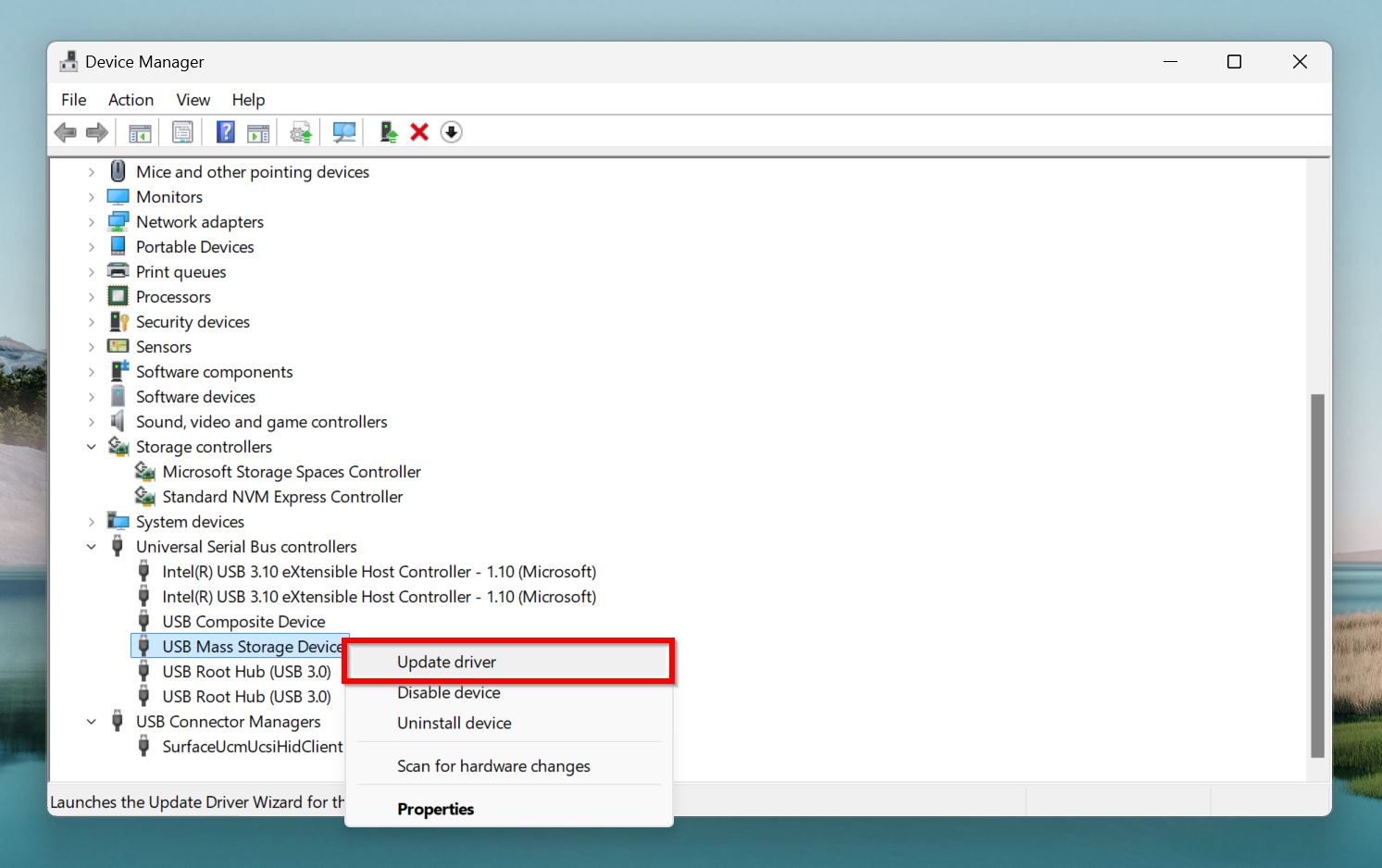
- Click on Search automatically for drivers.
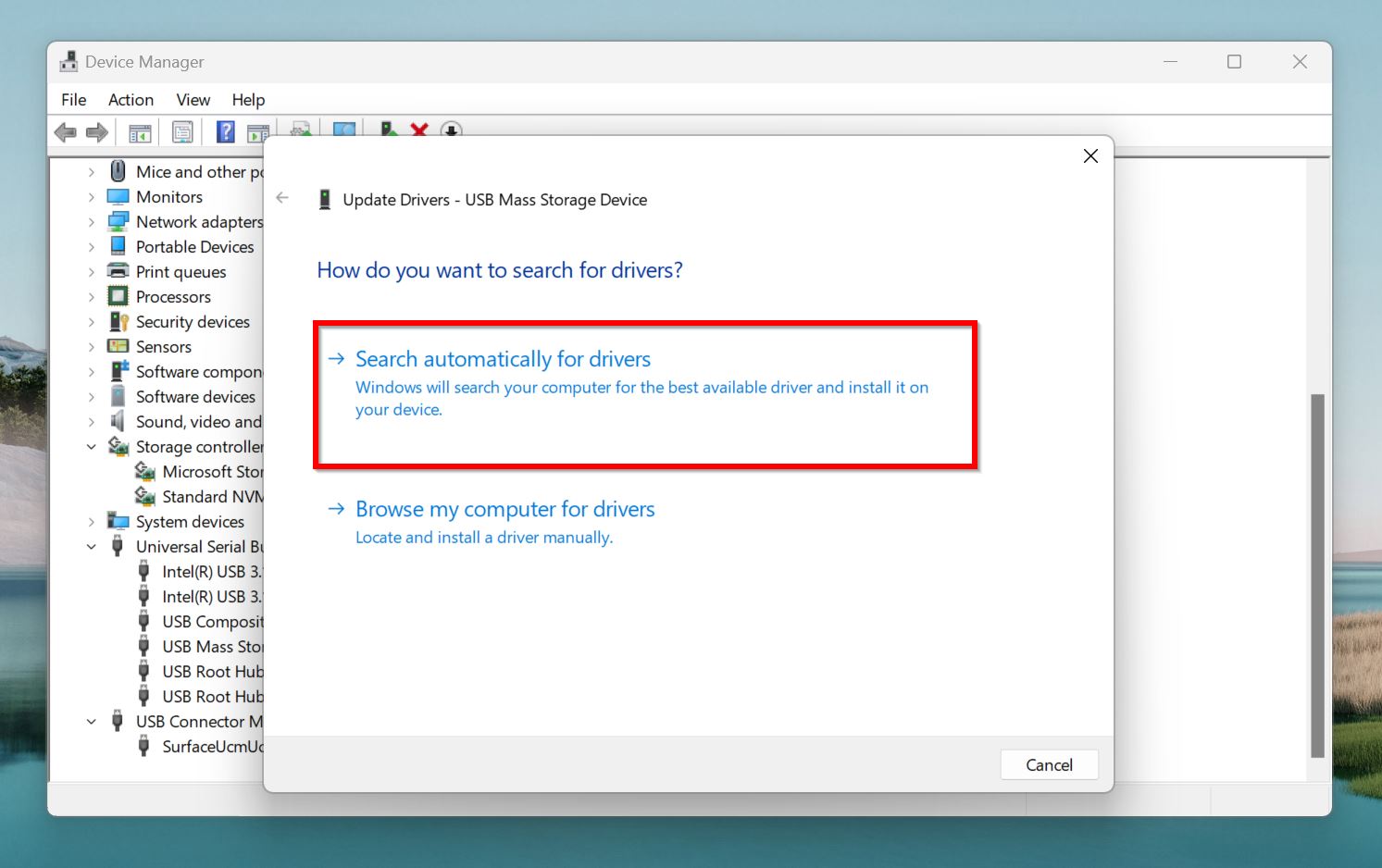
- Restart your PC.
Often, Windows won’t find the latest drivers for your SD card/SD card reader. In this case, manually download the latest drivers from the SD card, and SD card manufacturer’s website, and save it to your PC. Then, during Step 3 above, select Browse my computer for driver software, and double-click on the driver you downloaded.
Reinstall SD Card Drivers
- Open the Device Manager app. You can search for it in Windows Search (Windows Key + S), or open the Run app (Windows Key + R), type devmgmt.msc and press Enter.
- Expand the Disk Drives menu, and right-click on your SD card, and choose Uninstall device.
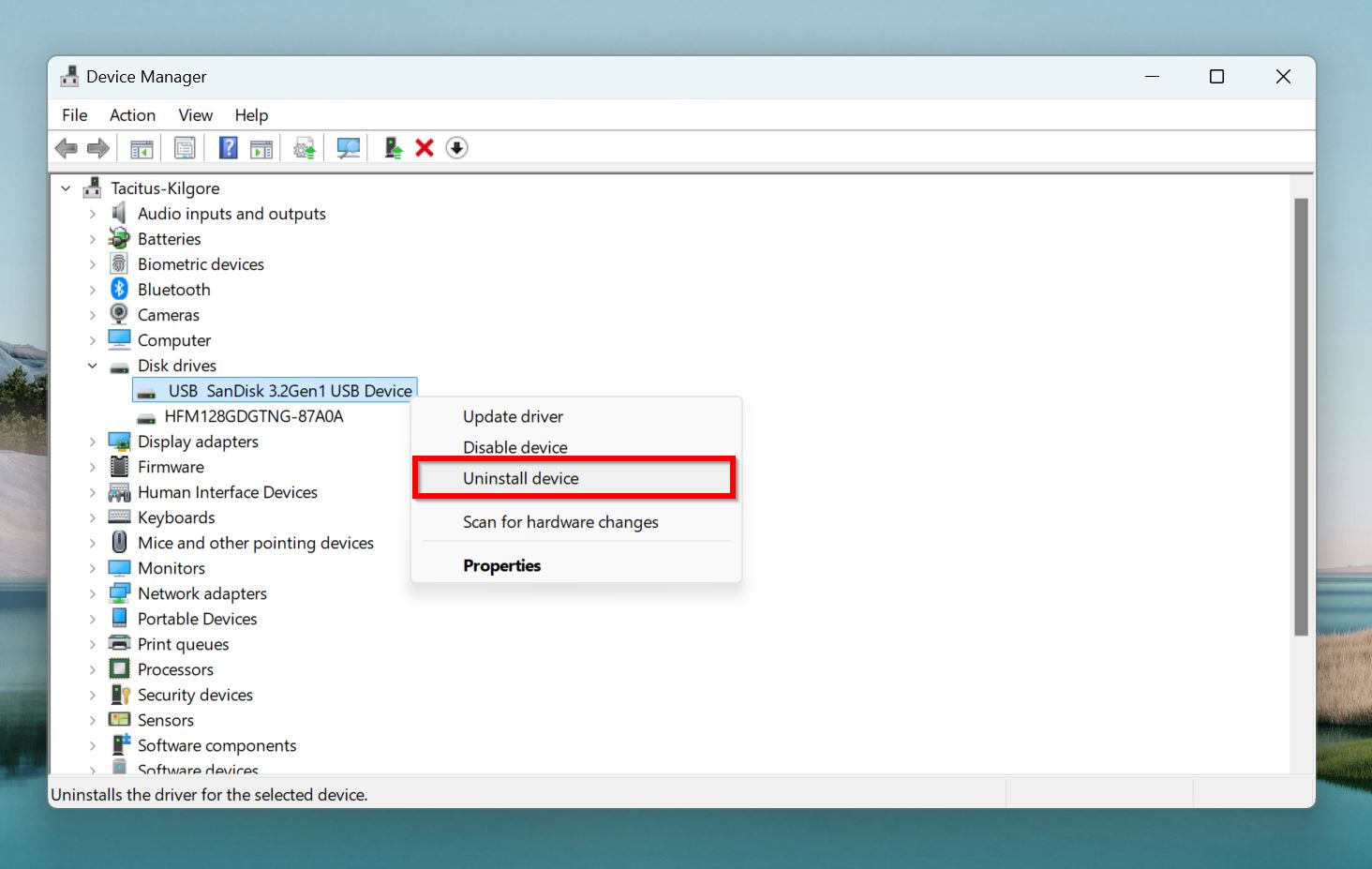
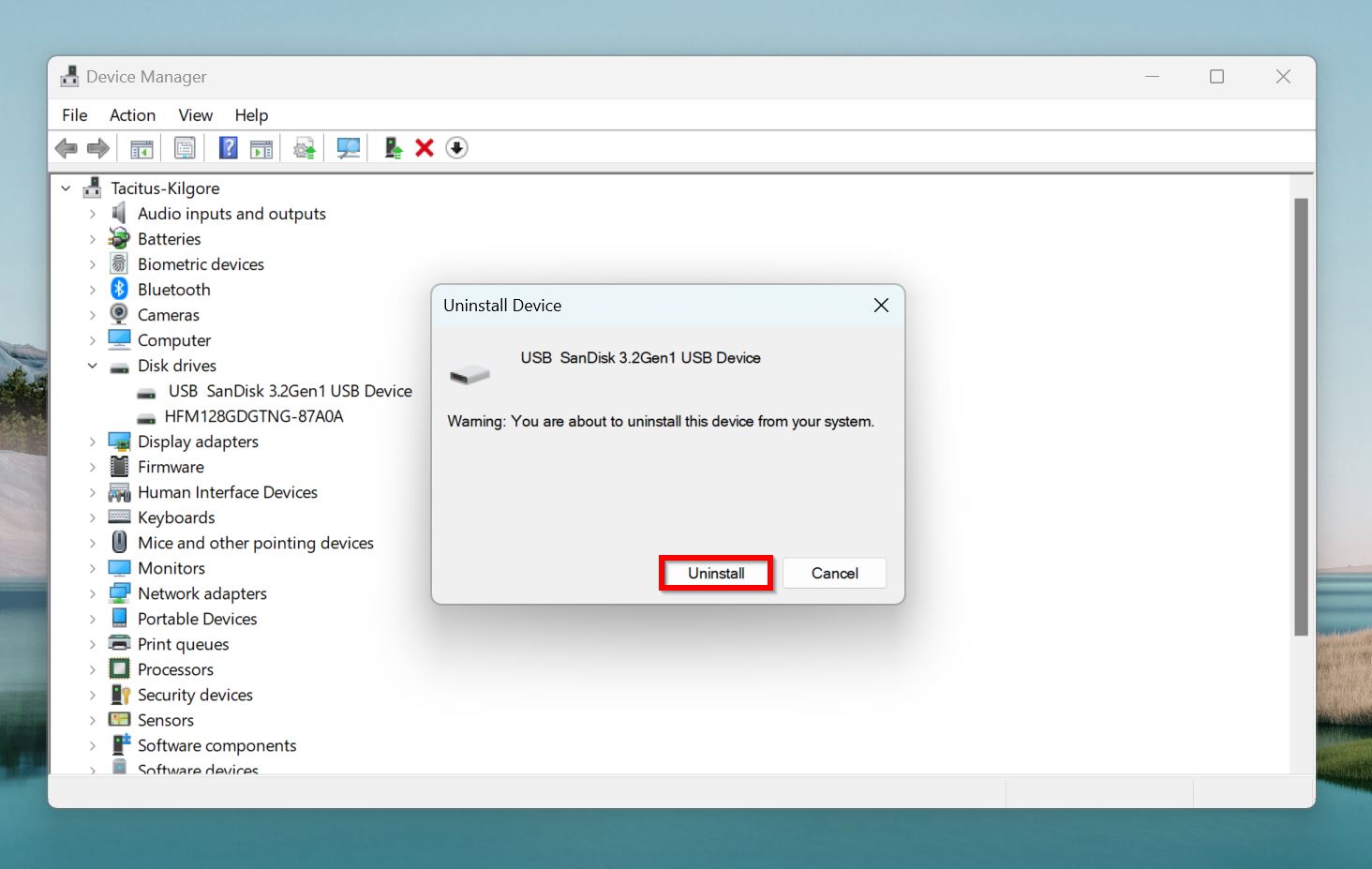
- Click on the Uninstall button in the next prompt. Leave the Delete driver software for this device option unchecked.
- Follow Step 2, and Step 3 for the SD card reader as well. If you don’t find it in the Disk Drives menu, look for it in the Universal Serial Bus Controllers, and Memory Technology Drivers menus.
- Restart your PC after Windows uninstalls the drivers.
- Open Device Manager after restarting, and see if the SD card and SD card reader are visible. If they aren’t, click on Action > Scan for hardware changes.
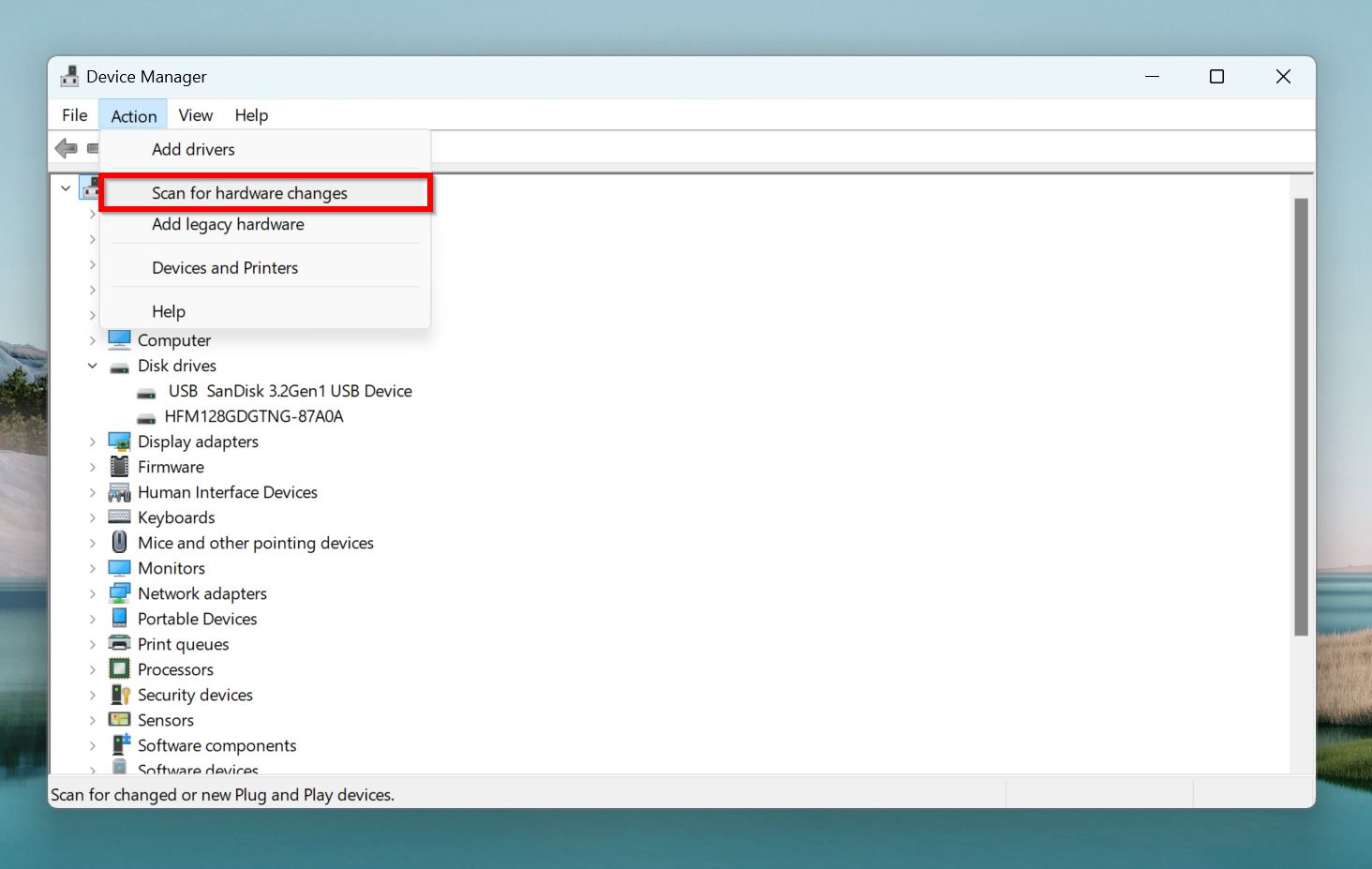
- Windows will refresh the system, and the SD card and card reader should appear.
Important: If your SD card keeps disconnecting from a SteamDeck with Windows installed, directly download the drivers from Steam Support and install them. In case you noticed data loss, we have a dedicated guide on recovering data from a SteamDeck.
Method 2: Uninstall Problematic Windows Updates
Once in a while, problematic Windows updates can cause SD card drivers to not work properly. If your SD card began acting up just around the time you updated Windows, find the problematic Windows update and uninstall it.
Here’s how:
- Right-click on the Start button and choose Settings.
- Click on Windows Update in the left navigation bar, and then click on Update history.
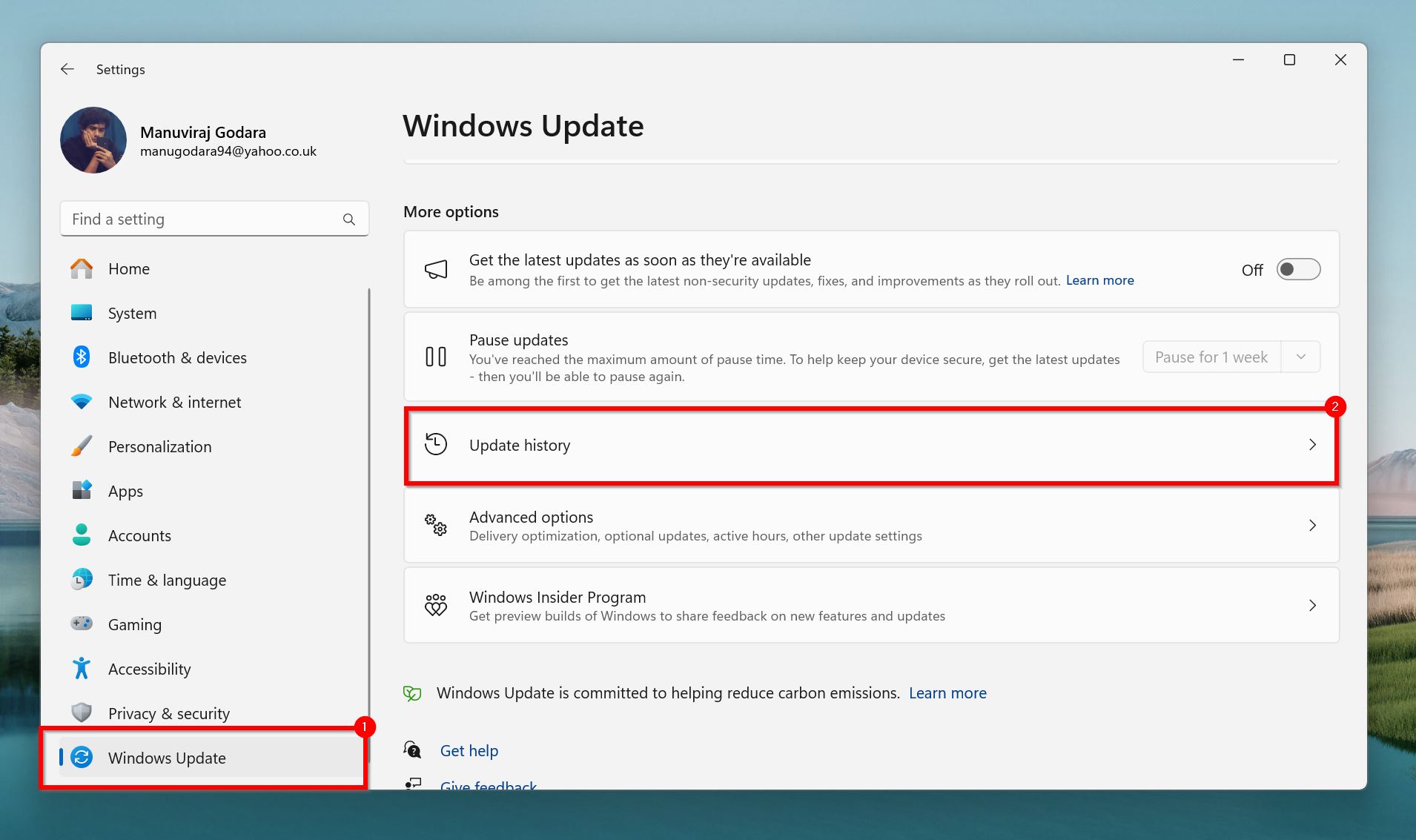
- Click on Uninstall updates, under Related settings.
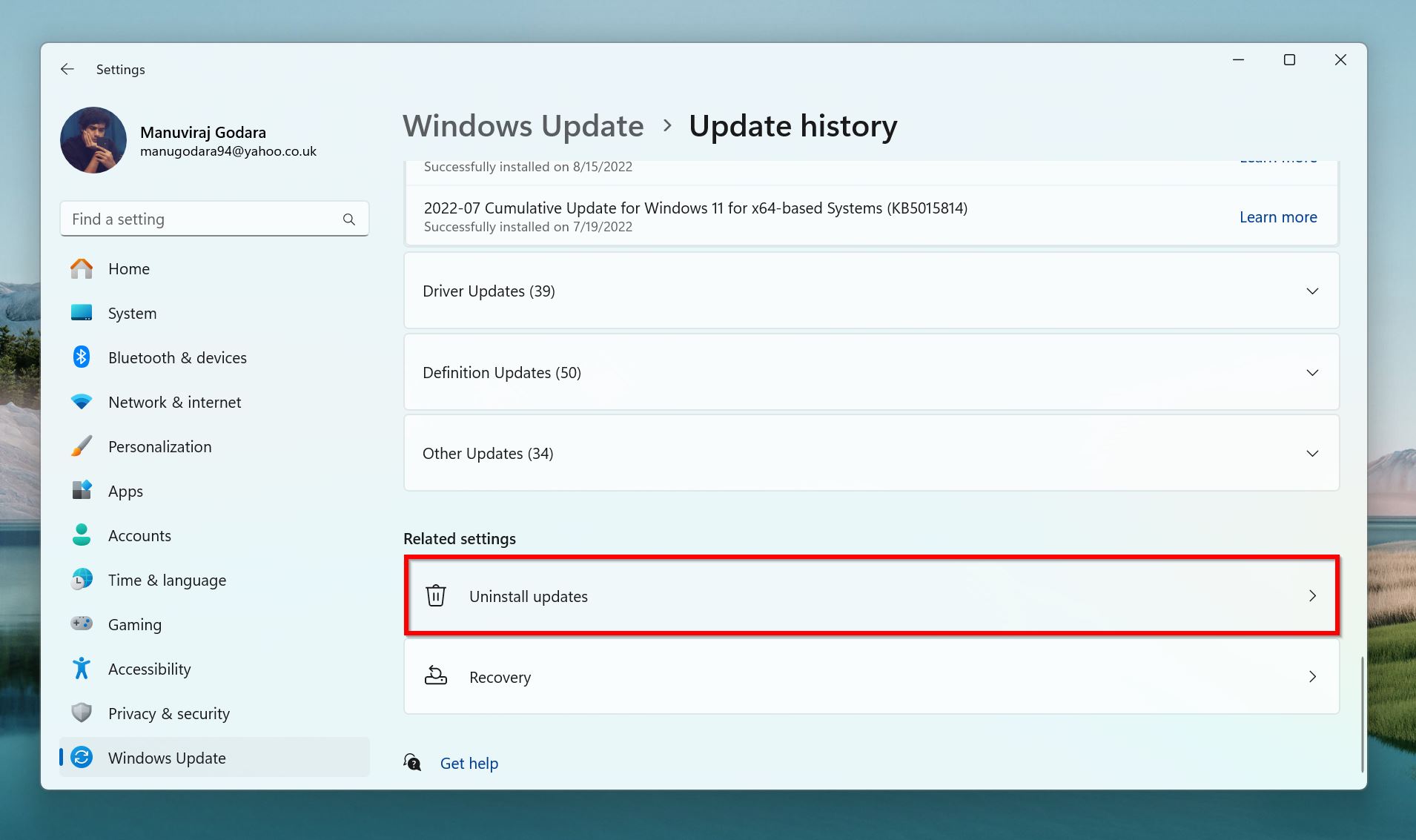
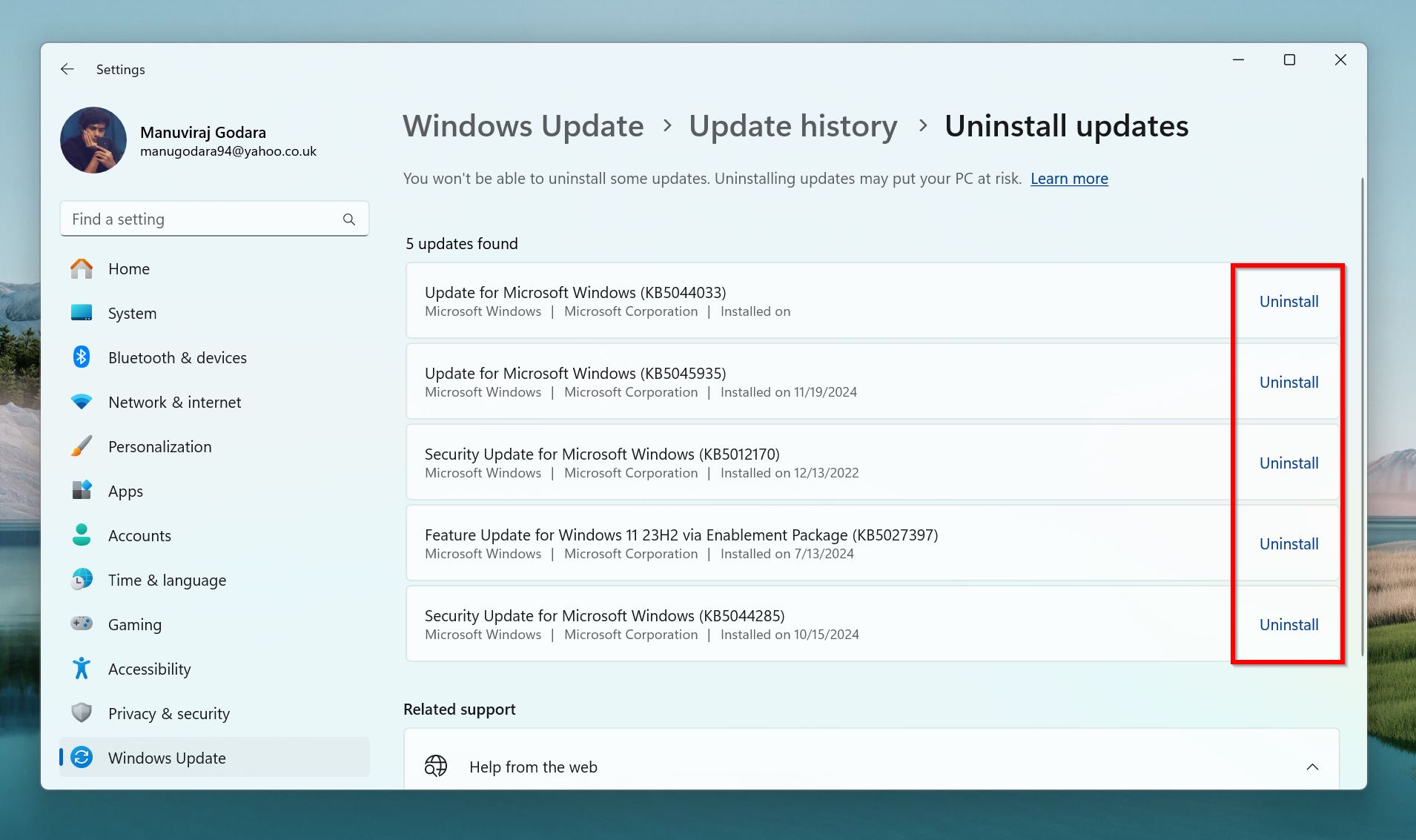
- Find the update you installed around the time your SD card began disconnecting, and click on Uninstall.
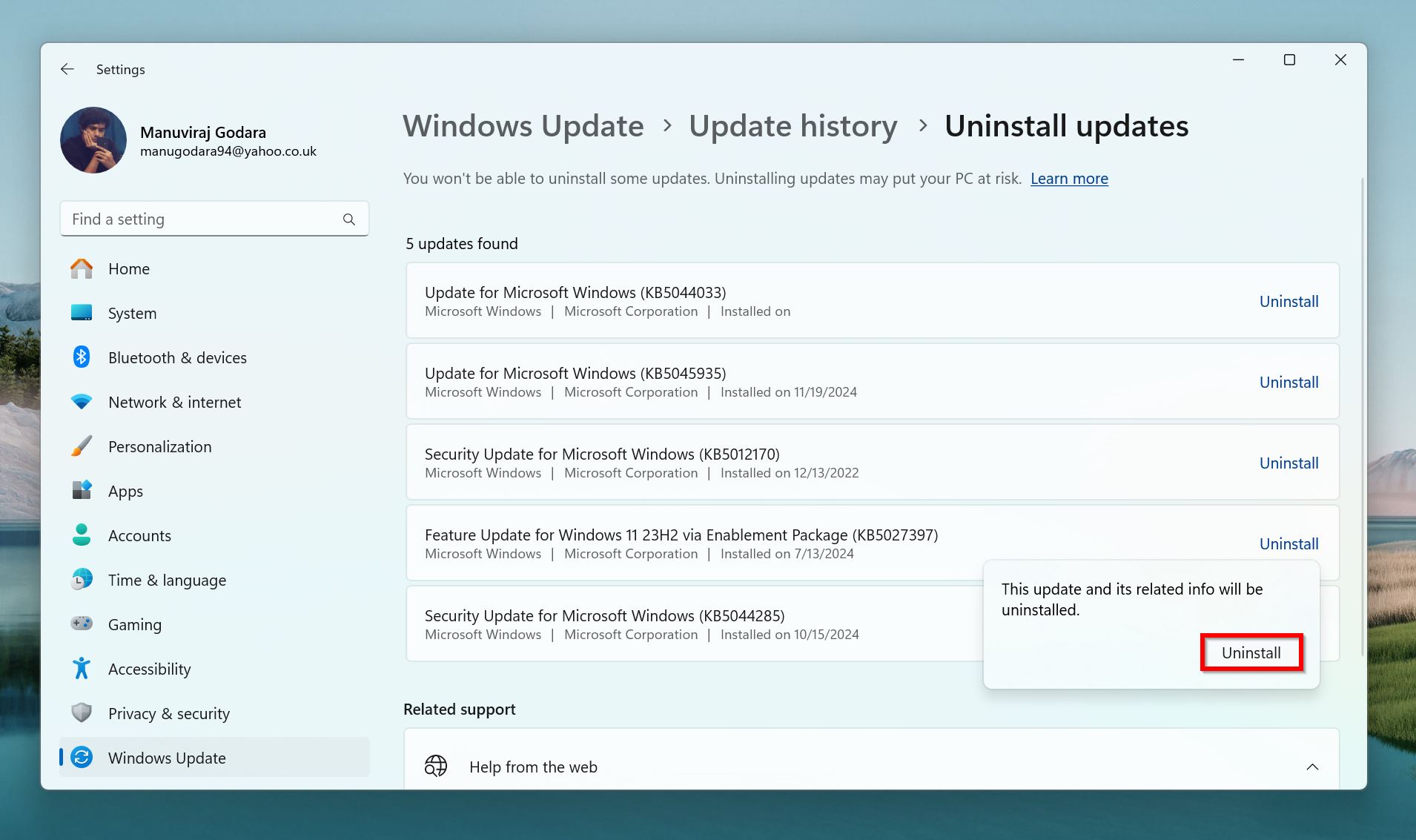
- Confirm by clicking Uninstall in the next pop-up.
- Reboot your PC.
Method 3: Change the SD Card’s Drive Letter
Each partition, and external drive on Windows, has a unique drive letter (C:, D:. E:. F:, etc.). Usually, Windows ensures that there aren’t any drive letter conflicts, but some bugs may cause two drives to have the same drive letter. When this happens, you’ll encounter several issues, including an SD card randomly disconnecting.
To fix the problem, manually assign a drive letter to the SD card. Here’s how:
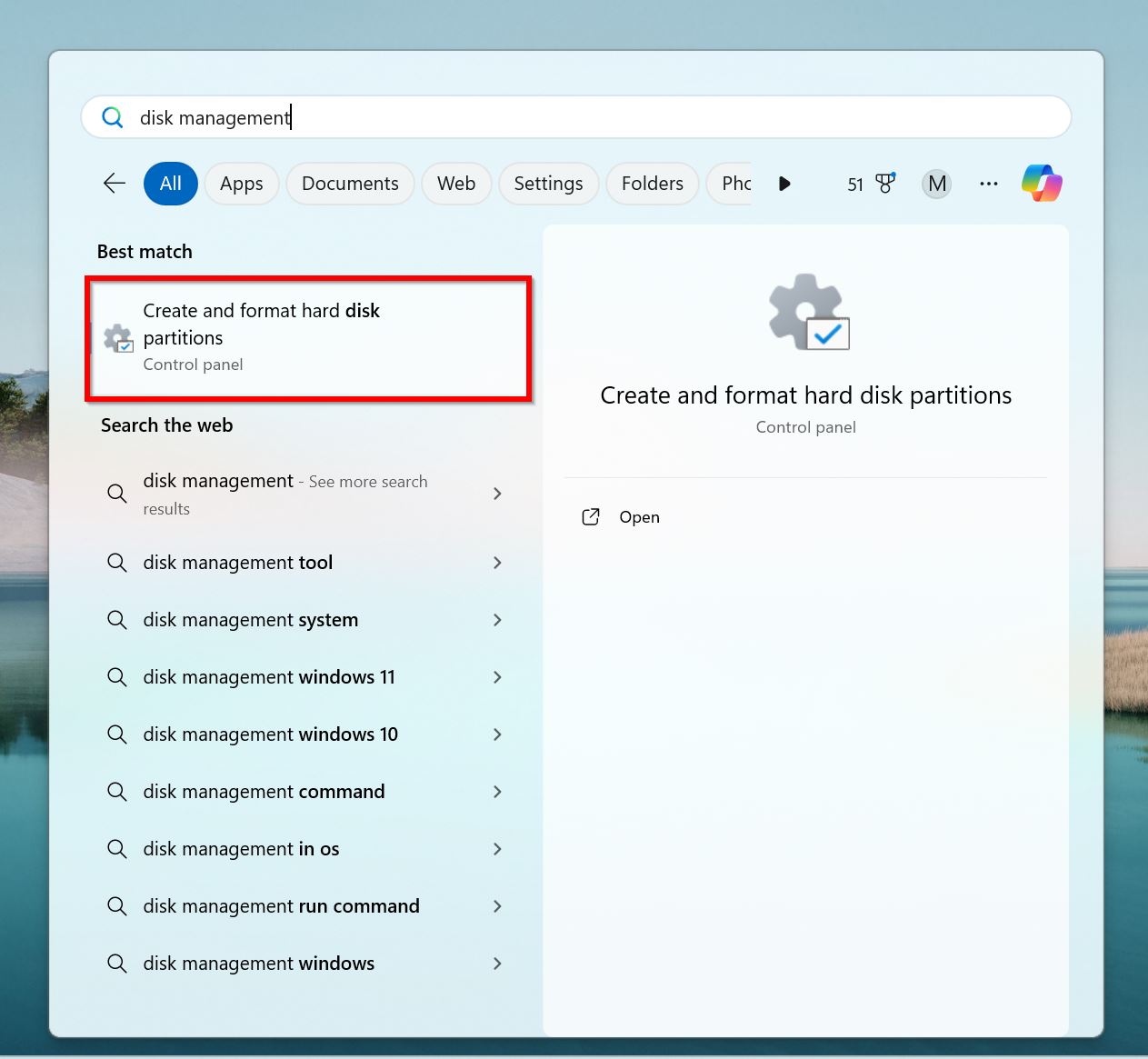
- Type disk management in Windows Search (Windows Key + S), and click on Create and format hard disk partitions from the search results.
- Right-click on the SD card, and select Change Drive Letter and Paths.
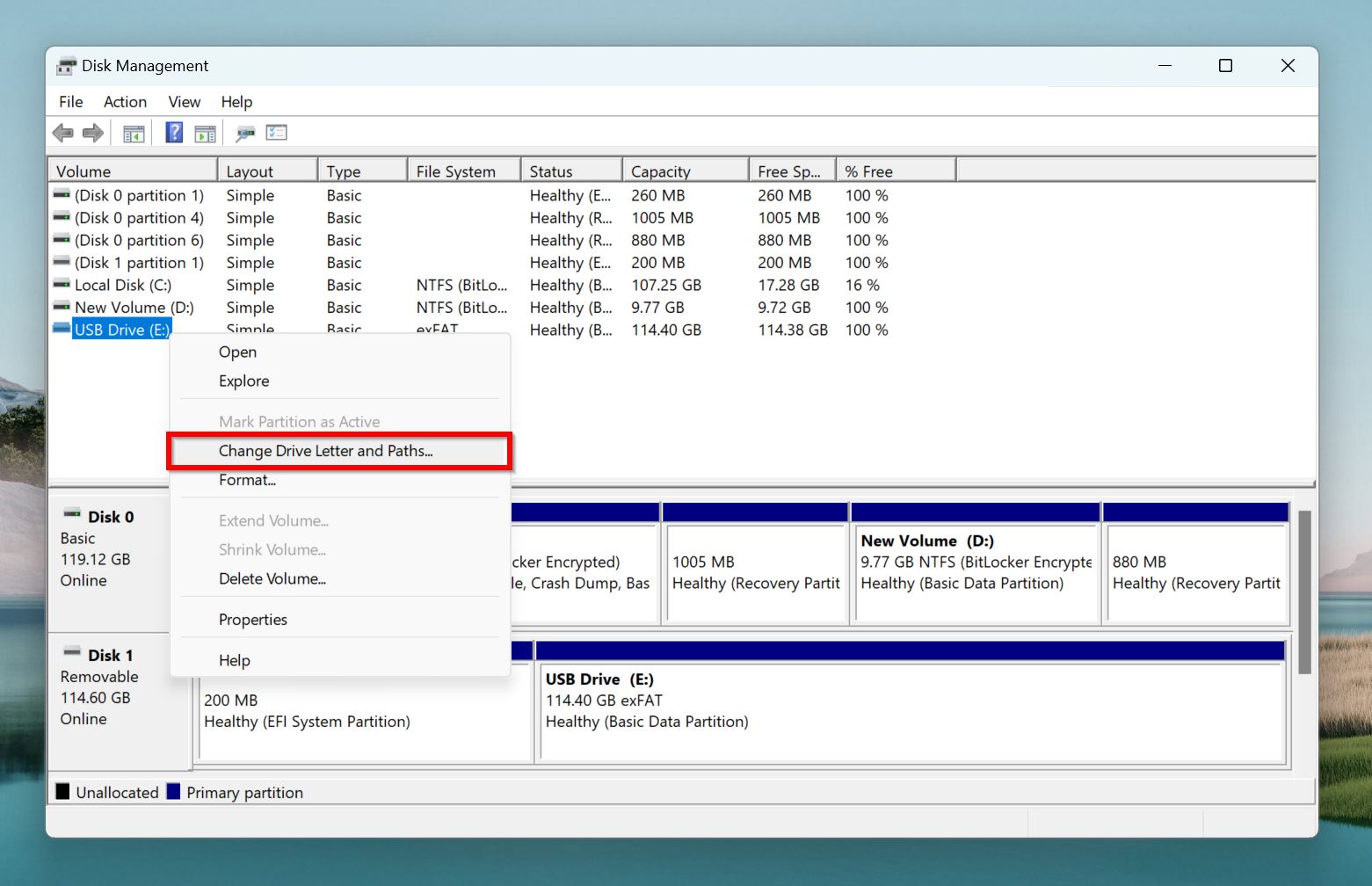
- Click on Change in the next prompt.
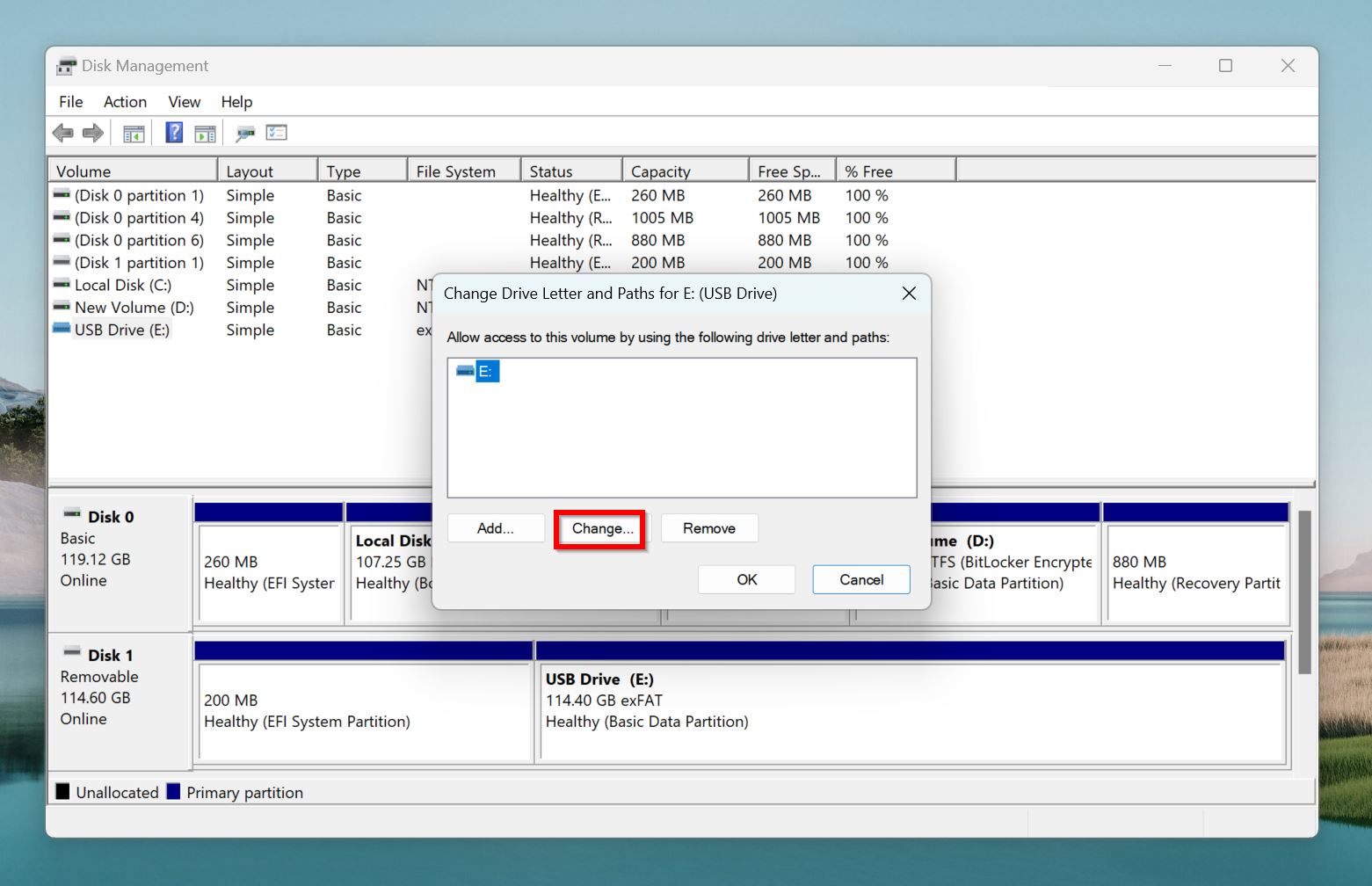
- Choose a different drive letter from the Assign the following drive letter drop-down menu.
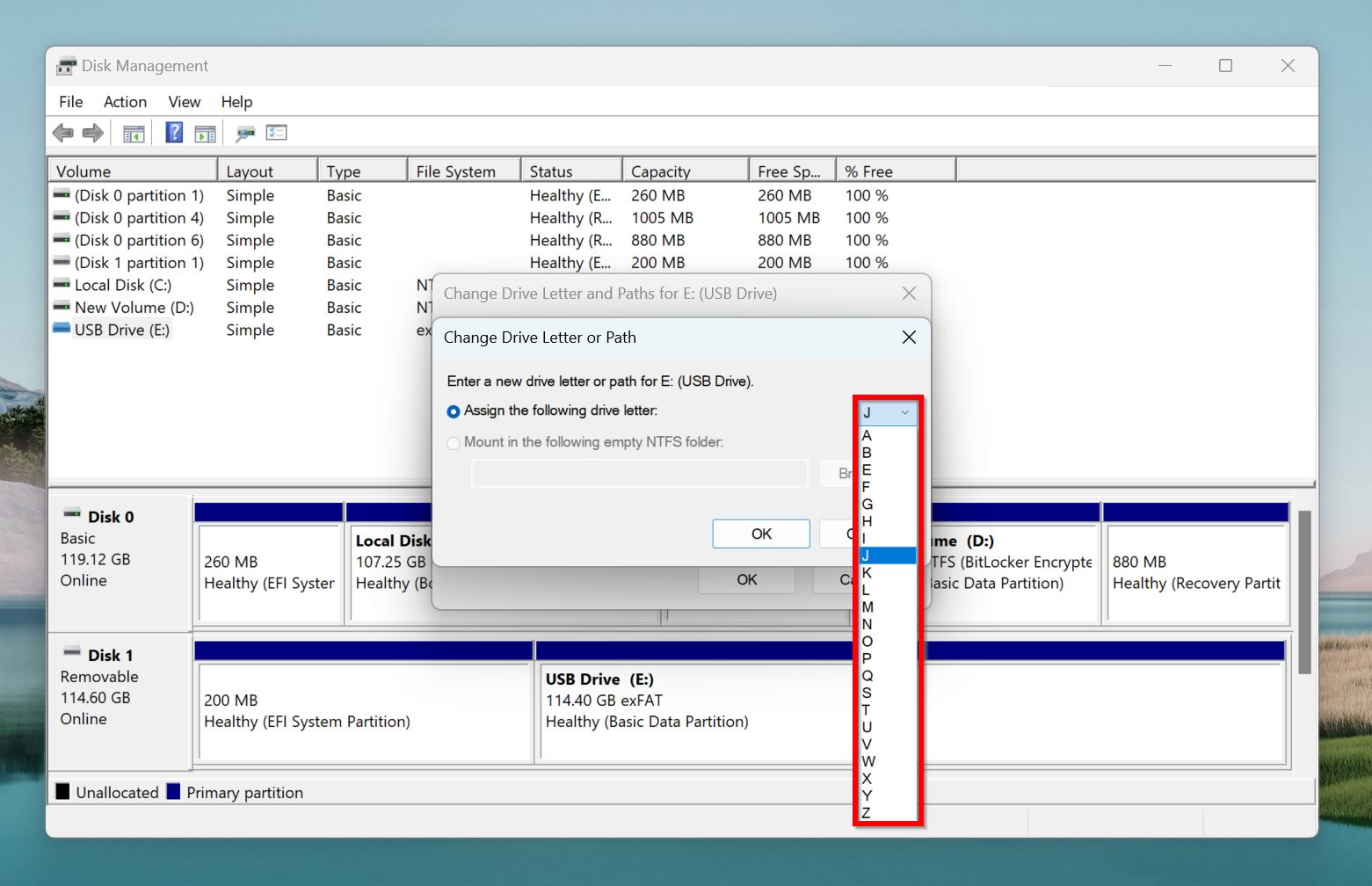
- Click on OK.
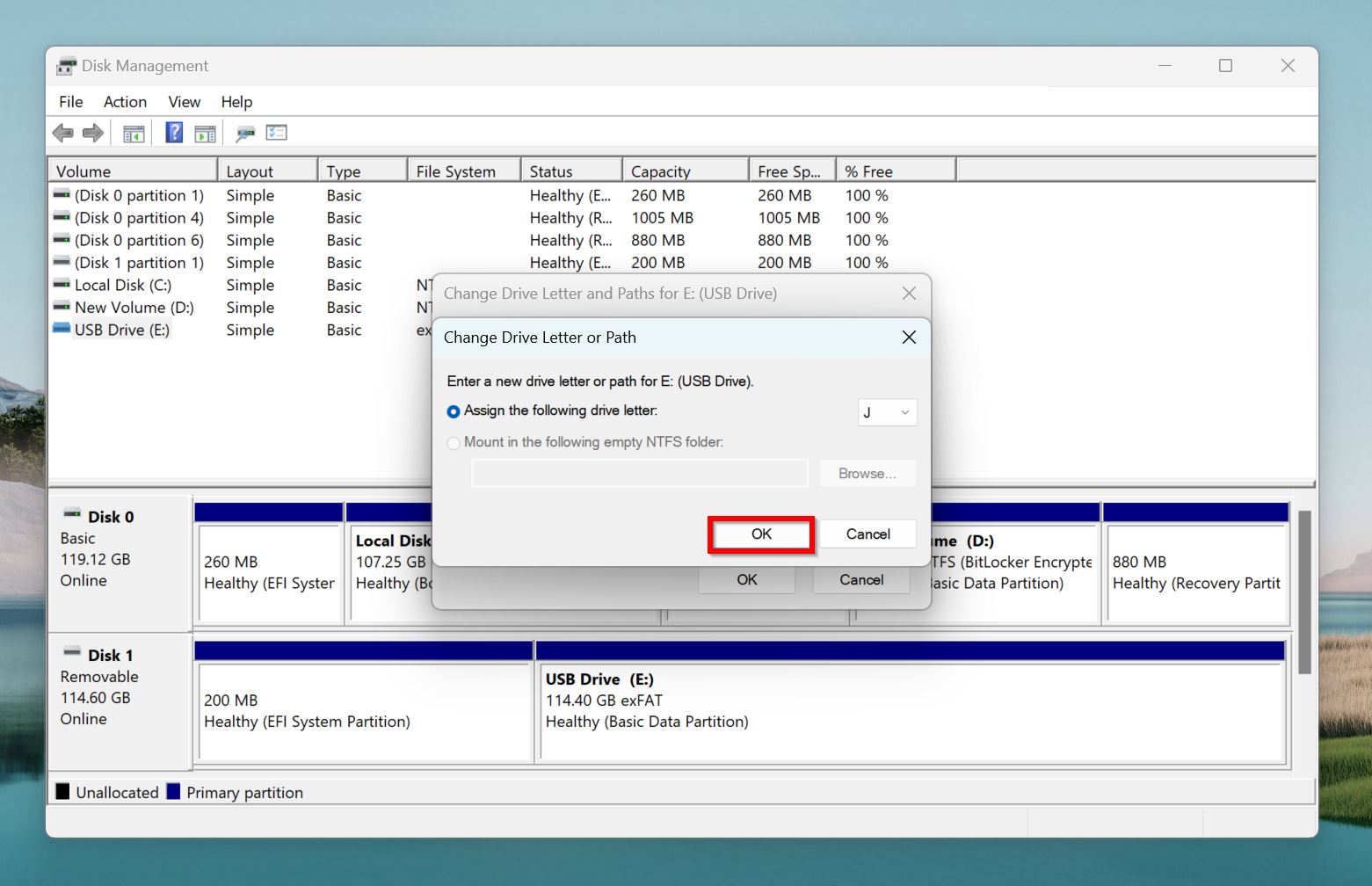
- Restart your PC, and reconnect the SD card.
Method 4: Configure Power Plan Settings
Windows has a feature, USB Selective Suspend, that automatically puts your computer’s USB ports in a low-power state when inactive. Often, Windows may run into trouble re-enabling the peripheral, or storage drive (like an SD card connected using a card reader) connected to the USB port. When this happens, your SD card will remain disconnected, until you reconnect it.
USB Selective Suspend is enabled by default. To disable it, follow this quick guide:
- Search for device manager in Windows Search (Windows Key + S), and open Device Manager from the search results.
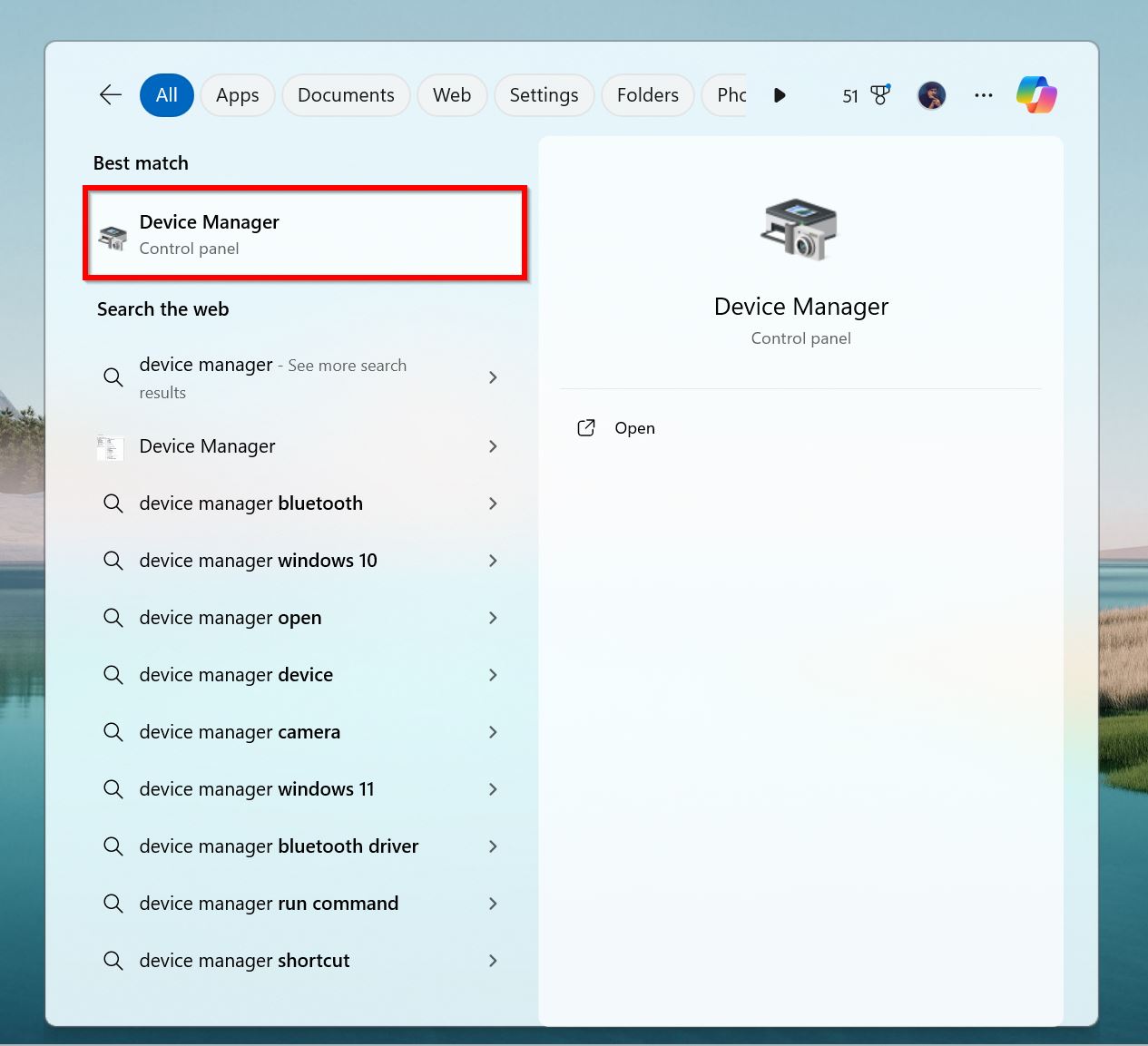
- Expand the Universal Serial Bus Controllers section.
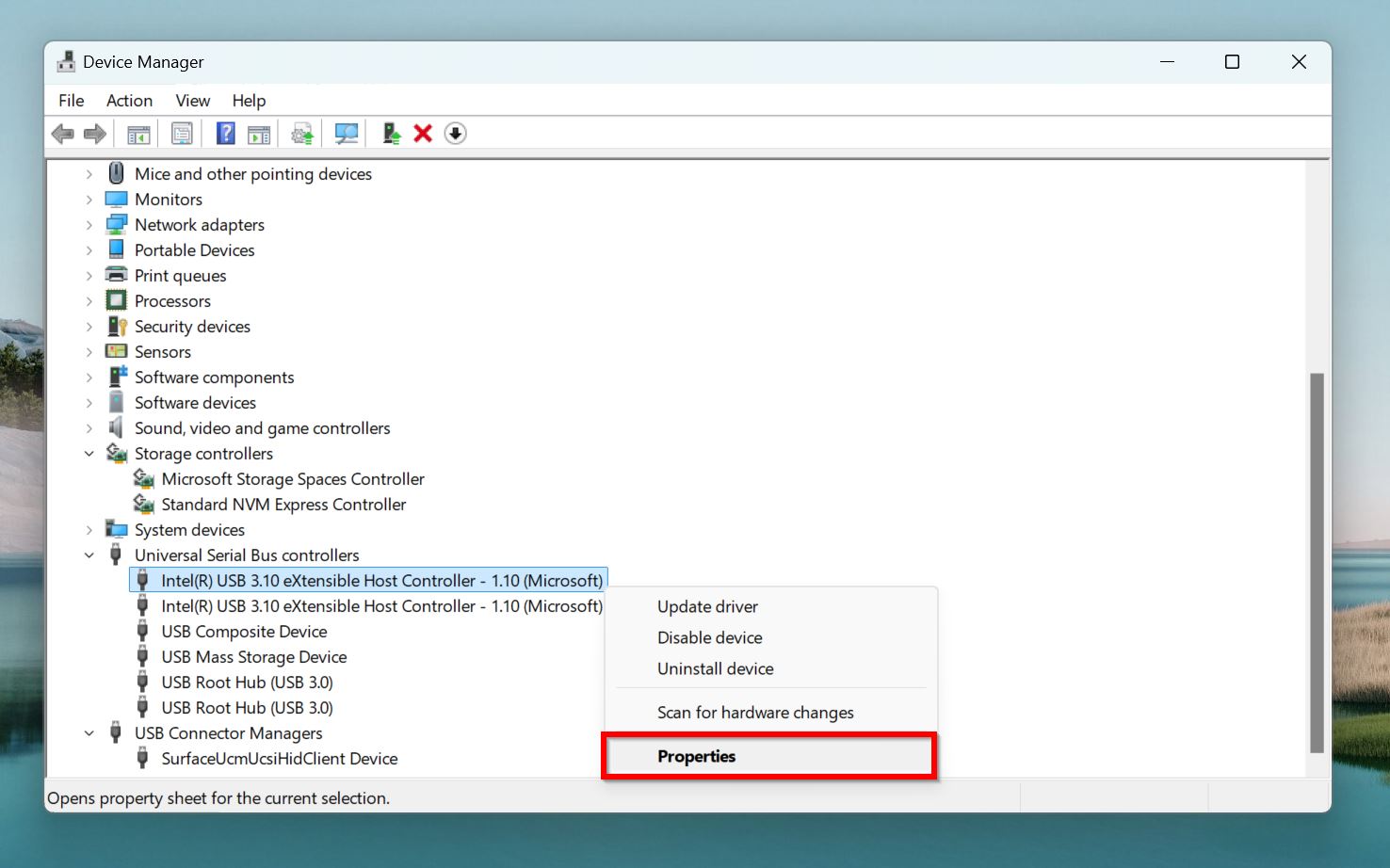
- Right-click on a USB Root Hub, and click Properties.
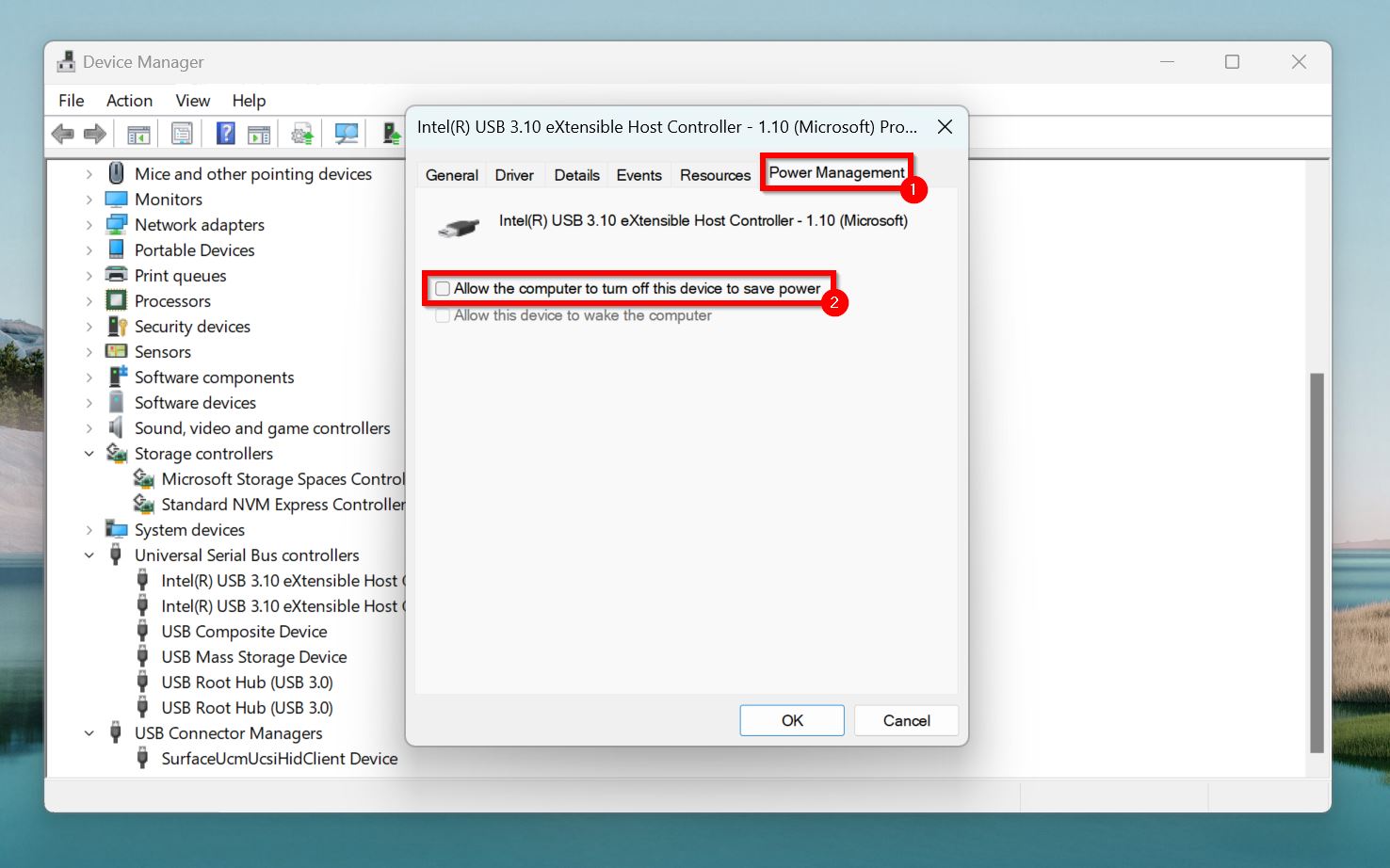
- Go to the Power Management tab, and uncheck the Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power option.
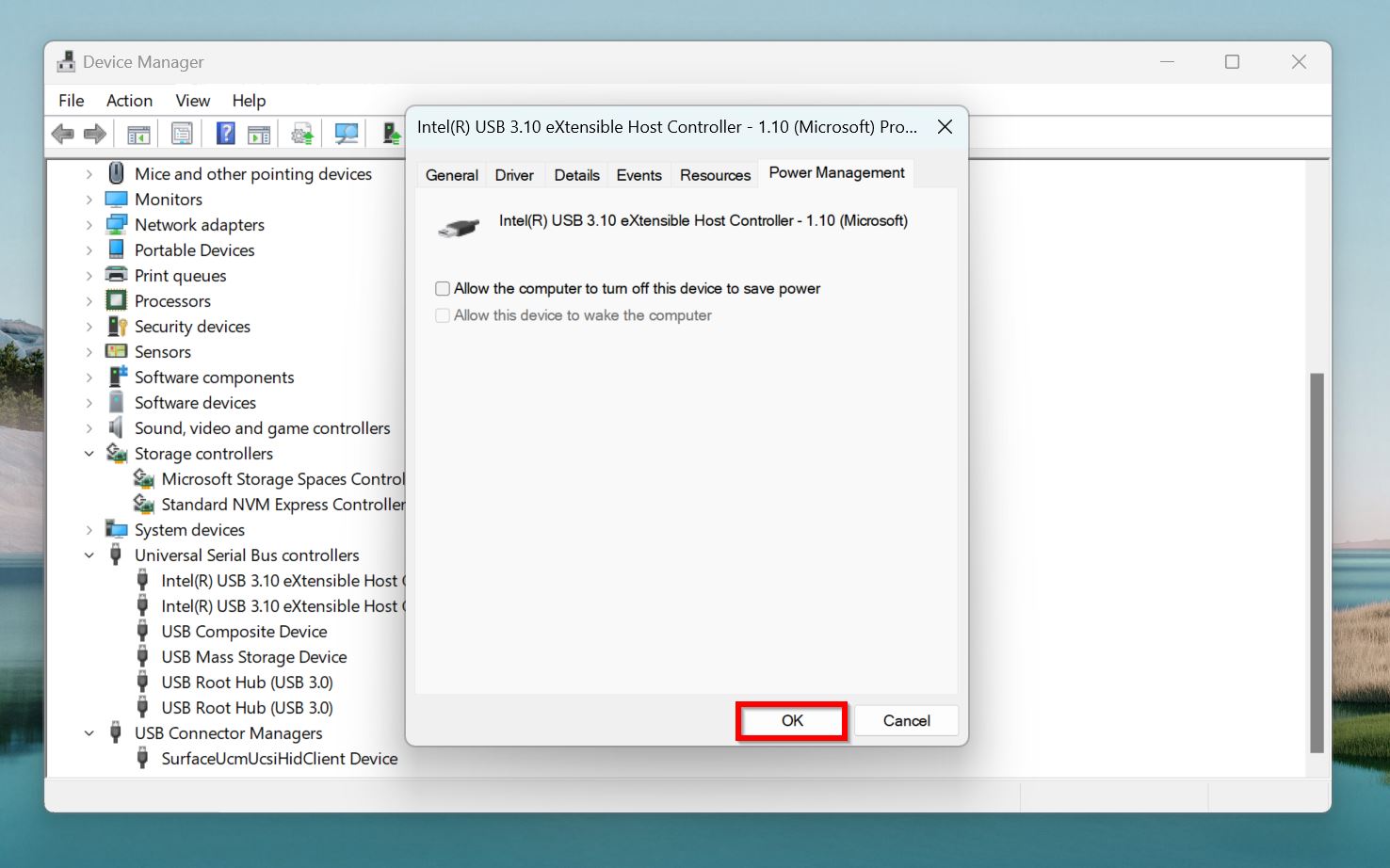
- Click OK.
- Follow Steps 3, 4, and 5 for each USB Root Hub.
- Reboot your PC.
Note: In case your SD card keeps disconnecting from your Android phone, check if the device is in power-saving mode. The low power mode on some Android devices can be extremely restrictive, and cause such issues.
Method 5: Run CHKDSK to Fix any File System Errors
Over time, most storage drives develop bad sectors or unreadable areas. An accumulation of bad sectors can cause several problems—including data loss, and frequent disconnections. While bad sectors can’t be reversed, you can use an in-built Windows utility, CHKDSK (Check Disk), to find these bad sectors and mark them as unavailable for use. This prompts Windows to avoid any read/write operations to these areas, resulting in smoother operation of the SD card.
Be warned, you may notice some minor data loss after running CHKDSK because Windows purges any data contained in the bad sectors. Think of it as collateral damage. It’s best to recover your data before attempting this method.
Here’s how to run CHKDSK and potentially fix an SD card that gets unmounted:
- Search for cmd in Windows Search (Windows Key + S). Right-click on Command Prompt and choose Run as administrator.
- Type chkdsk X: /r and press Enter. Replace X with the SD card’s drive letter (D:. E:, F:, etc.)—you can confirm this in Disk Management, or Windows Explorer.
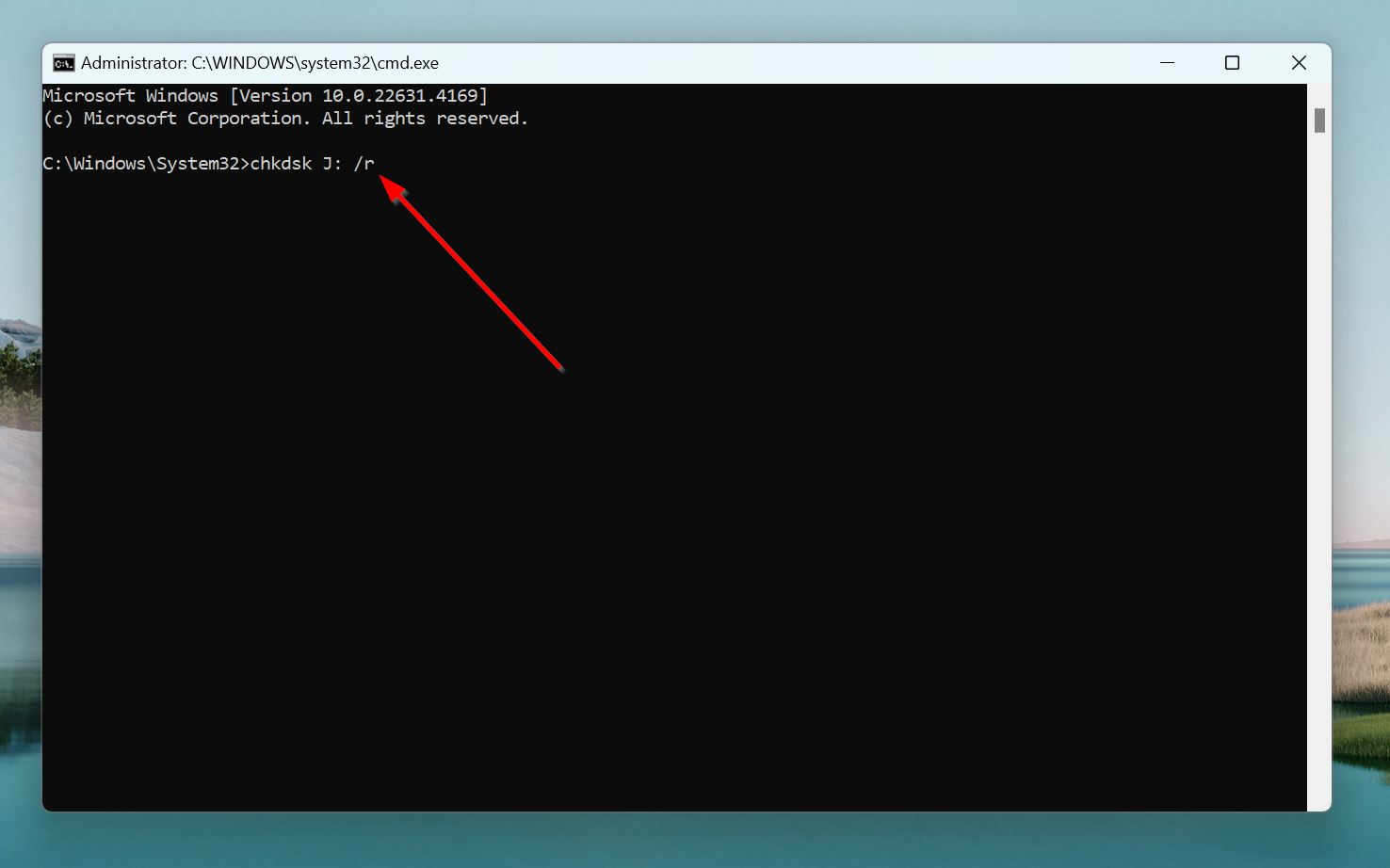
- Wait while Windows checks and repairs bad sectors on the SD card.
- Reboot your PC.
Note: If the SD card is damaged to the point that its file system becomes unrecognizable (RAW), CHKDSK won’t be able to scan it.
Method 6: Format the SD Card
Formatting the SD card practically gives you a clean slate—it rewrites the file system, and deletes all existing data from it. If your SD card keeps disconnecting due to logical errors, there’s a high chance that formatting it will fix the problem. While you can recover data from a formatted SD card (only if it’s a quick format), I still suggest backing up your data before proceeding.
Here’s how to format your SD card:
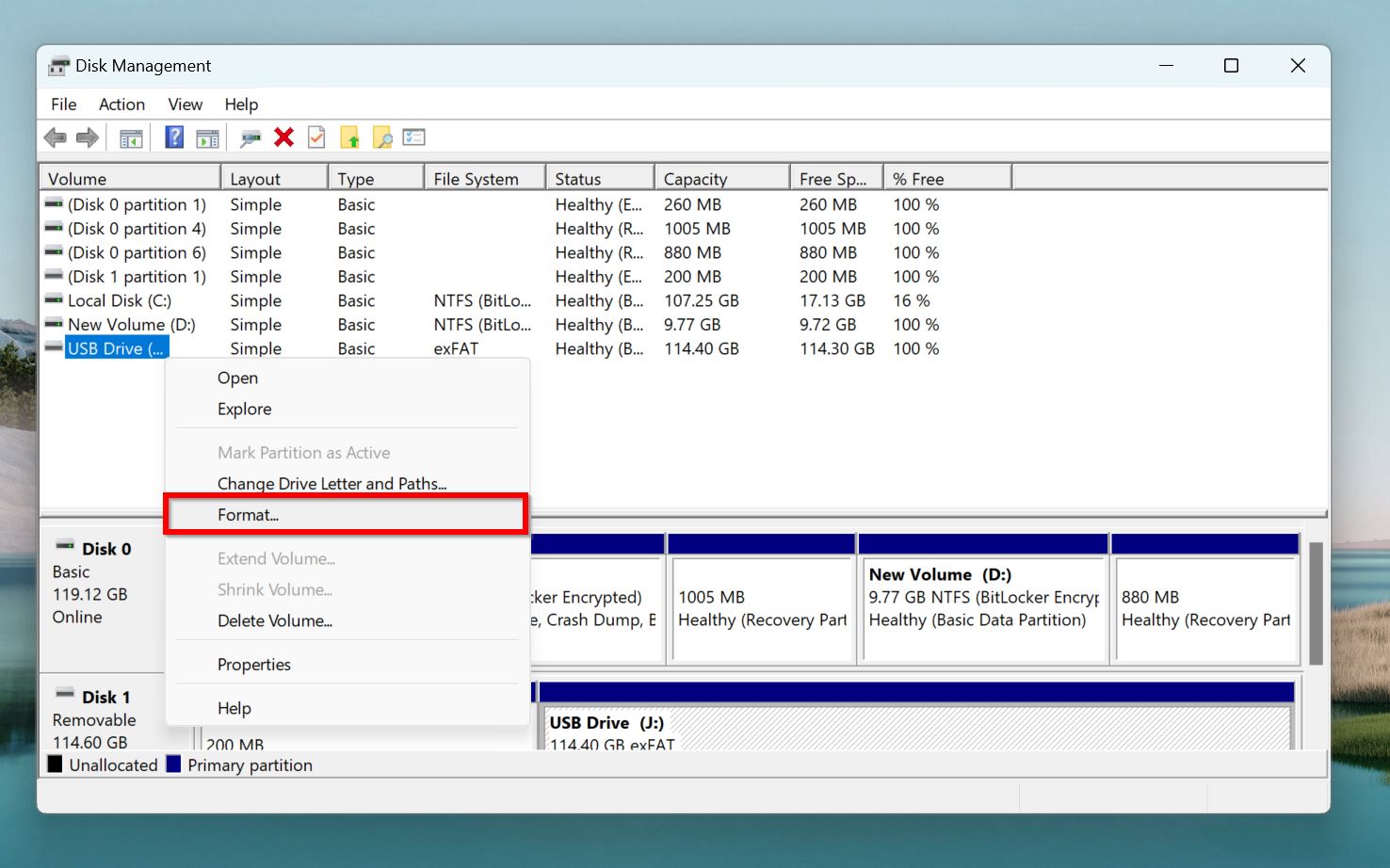
- Press Windows Key + R to open the Run app. Type diskmgmt.msc in the text box and press Enter.
- Right-click on the SD card from the storage drives list, and choose Format.
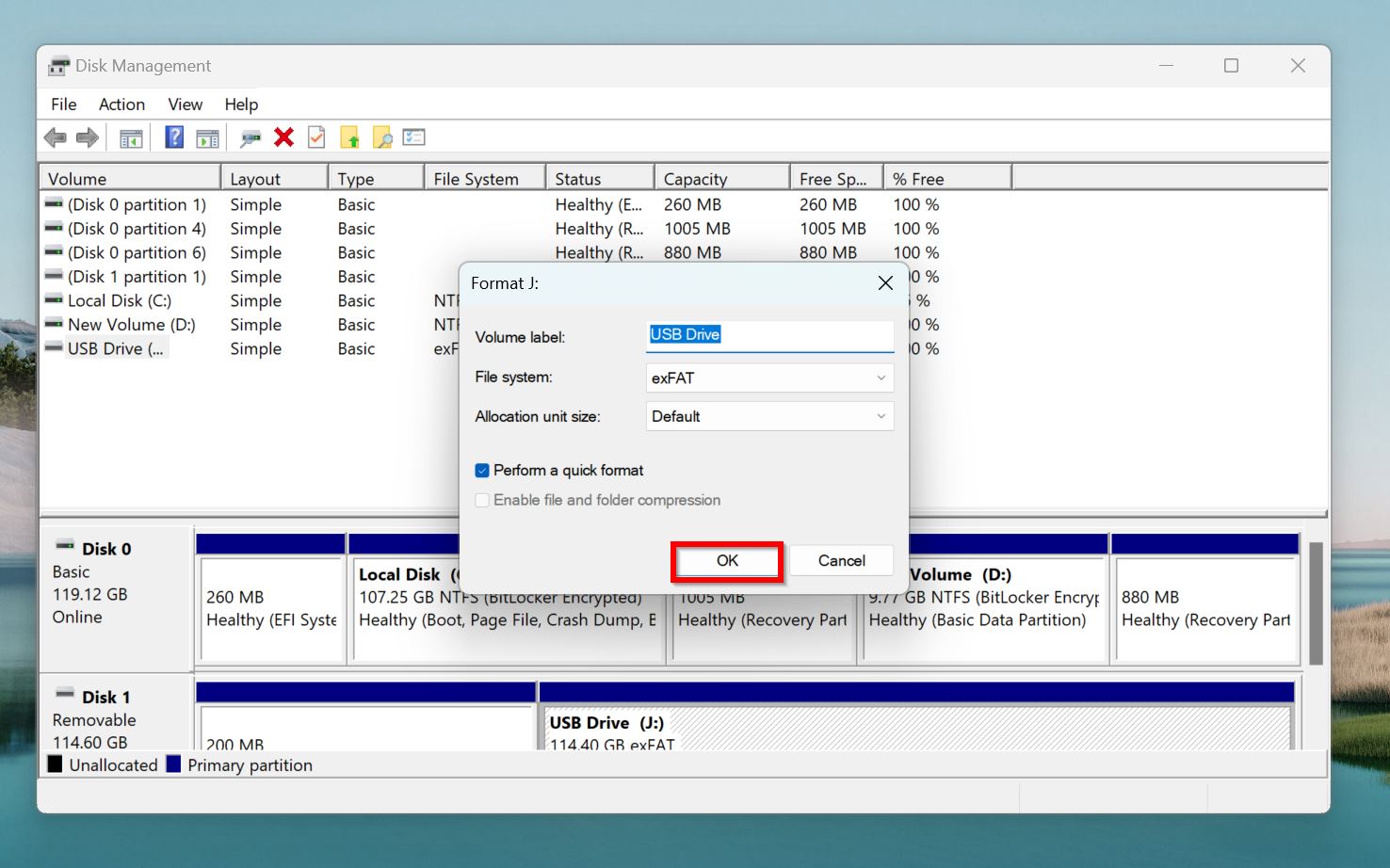
- Select the required file system from the File system drop-down menu. Click OK.
- Let Windows format the SD card, then reboot your PC.
Note: A common piece of advice floating on the internet is to format the SD card to the NTFS file system to fix the problem. Not only does it not work, but I don’t recommend doing that because most SD cards are used across cameras and other devices that may not recognize the NTFS format. I suggest sticking to the exFAT, and FAT32 file systems on SD cards because of their wider compatibility.
In case you’ve already formatted the SD card, keep in mind that reformatting it from one file system to another (like exFAT to NTFS) is less destructive than reformatting it to the same file system (exFAT to exFAT). In the latter case, data recovery programs will primarily rely on file signatures to recover your data and usually won’t recover your files with their metadata (file name, folder structure, modification history, etc.) intact.
Conclusion
The first step to fixing an SD card that keeps ejecting, is determining if the issue is hardware-based, or software-based. If the SD card is physically damaged, take it to a professional—DIY fixes rarely help in this case. But, if the SD card is in perfect physical condition—try updating the relevant drivers, changing the SD card’s drive letter, configuring your device’s power settings, running CHKDSK, and finally, formatting the affected SD card.
FAQ
How can I tell if my SD card is fake?
Fake SD cards usually have these telltale signs:
- Spelling mistakes, and other discrepancies on the packaging.
- SD cards that advertise extreme storage capacities, like 512 GB, at a throwaway price, are usually fake. It’s best to verify the storage capacity that’s being advertised.
- While it could be a defective SD card too, most counterfeit SD cards have abysmal performance. Copying and reading files will take much longer than it should. Use a tool like CrystalDiskMark to verify that you’re getting the stated read/write speeds.
Can a virus cause my SD card to keep disconnecting?
Yes, but not directly. Malware can corrupt your SD card’s file system, and impact Windows’ ability to read the SD card.
How can I safely eject my SD card to prevent damage?
You can use the safe eject feature on Windows, macOS, Android, or your camera to safely eject an SD card before physically disconnecting it. Here’s how:
- On Windows: Open File Explorer (Windows Key + E), right-click on the SD card, and click Eject.
- On macOS: Right-click on the SD card icon on your desktop, or in Finder, and click Eject.
- On Android: Go to Settings > Storage, and click Unmount next to the SD card.
- On a camera: This differs across manufacturers. Check the user manual to know the exact steps.
This article was written by Manuviraj Godara, a Staff Writer at Handy Recovery Advisor. It was also verified for technical accuracy by Andrey Vasilyev, our editorial advisor.
Curious about our content creation process? Take a look at our Editor Guidelines.
